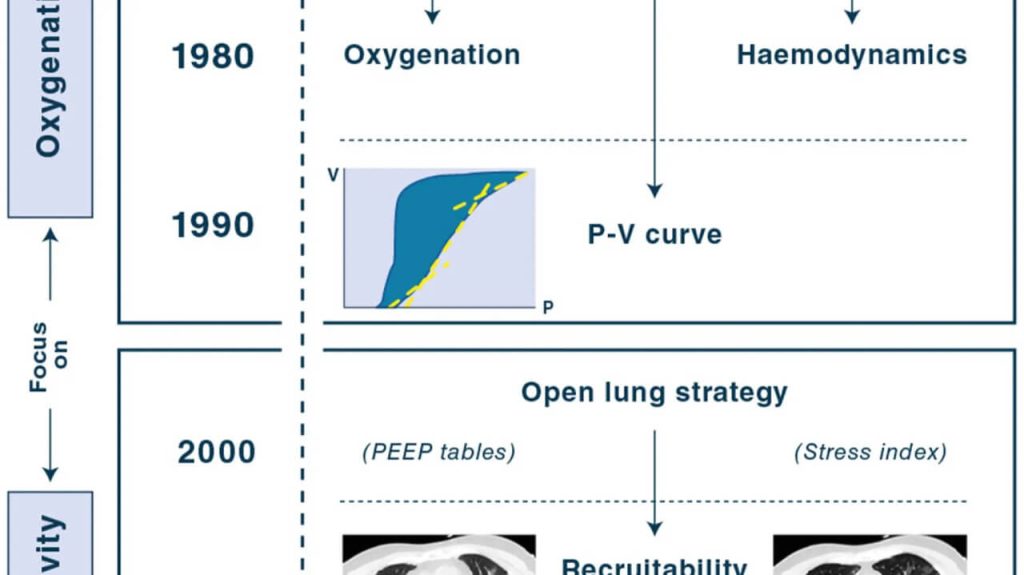
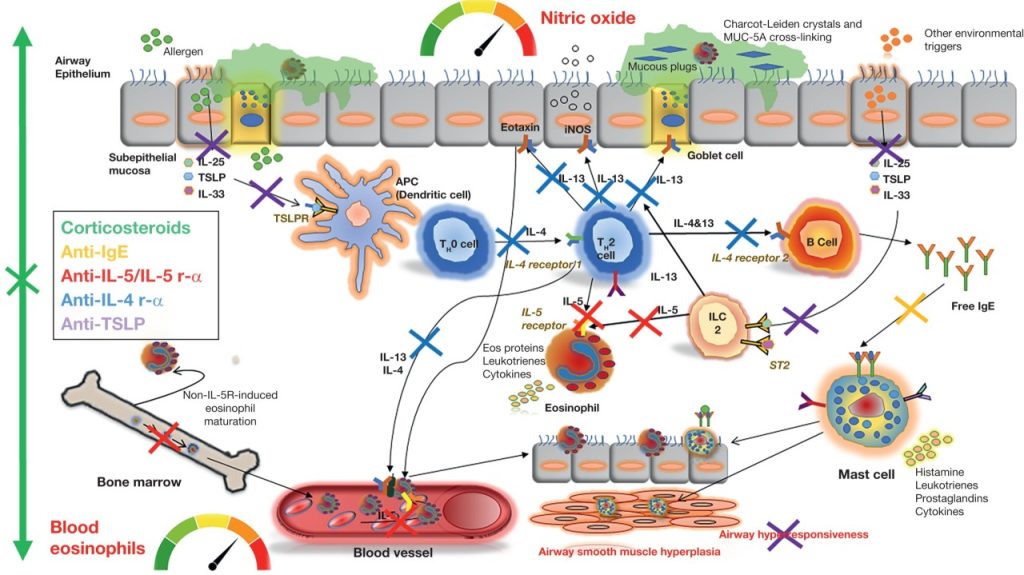
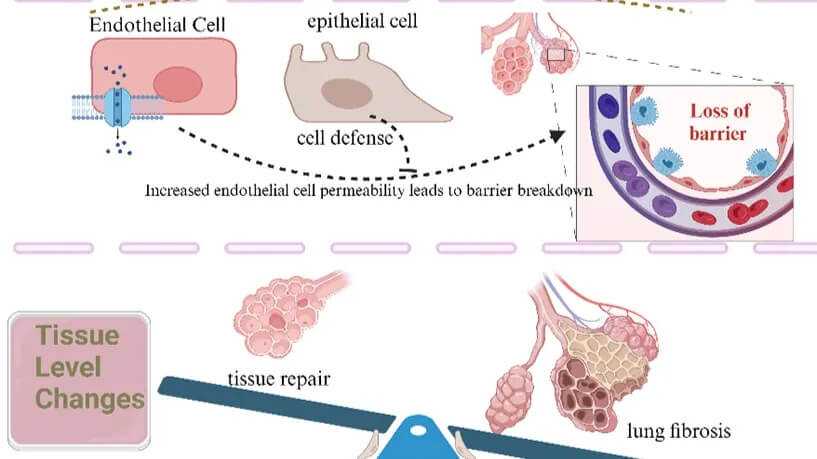
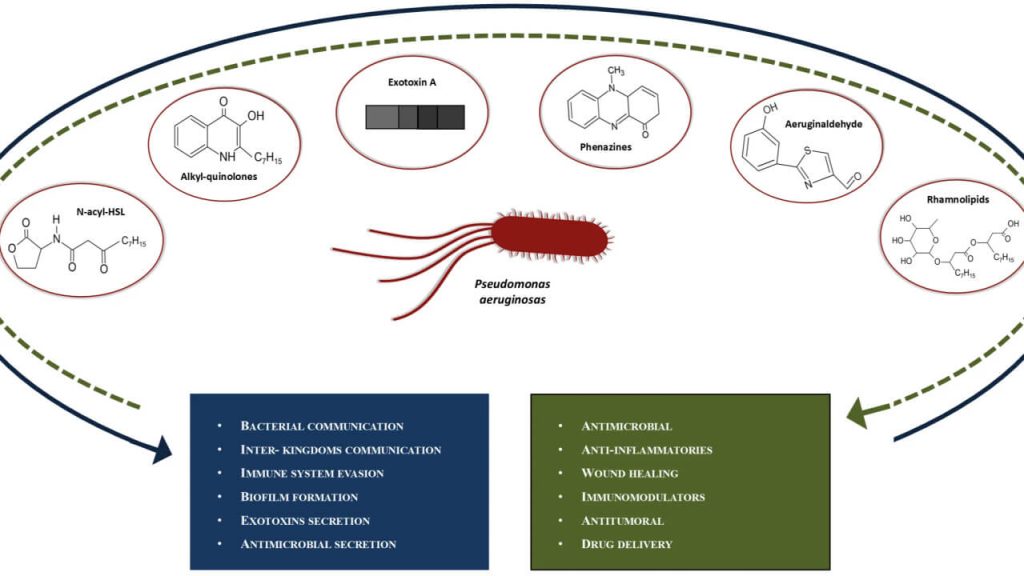
How I personalize fluid therapy in septic shock?
Abstract During septic shock, fluid therapy is aimed at increasing cardiac output and improving tissue oxygenation, but it poses two problems: it has inconsistent and transient efficacy, and it has many well-documented deleterious effects. We suggest that there is a place for its personalization according to the patient characteristics and the clinical situation, at all […]
How I personalize fluid therapy in septic shock? Read Post »