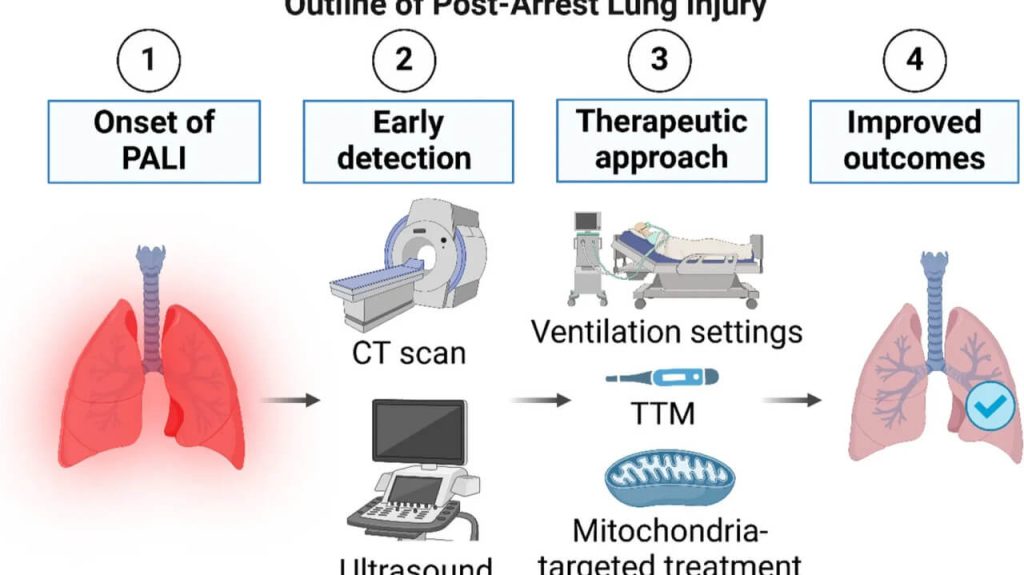
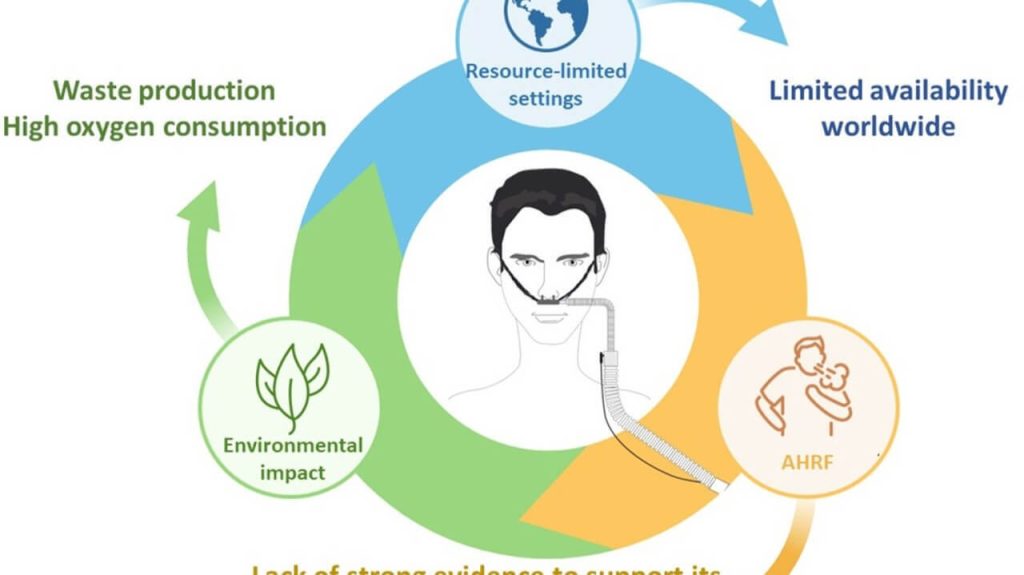
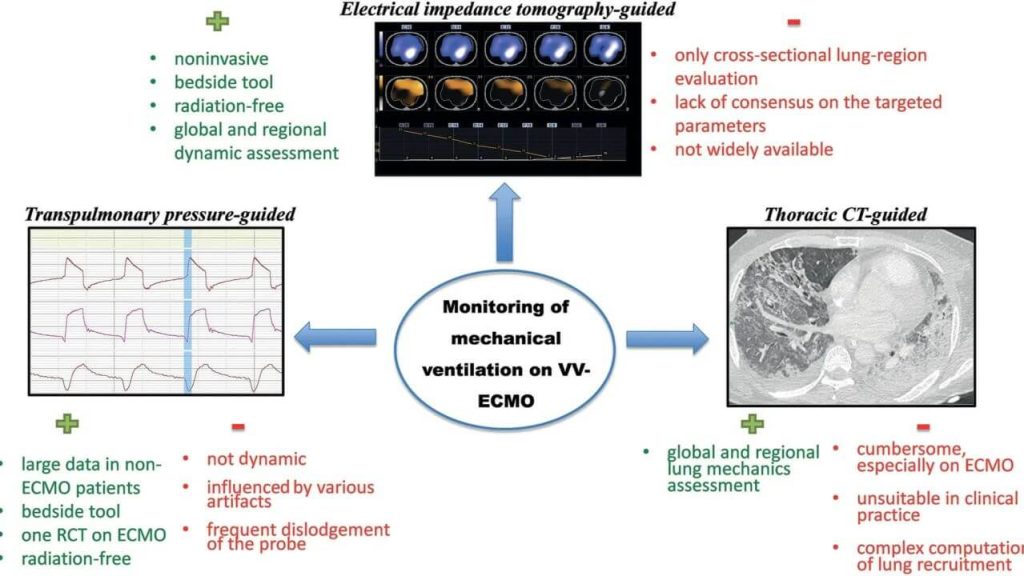
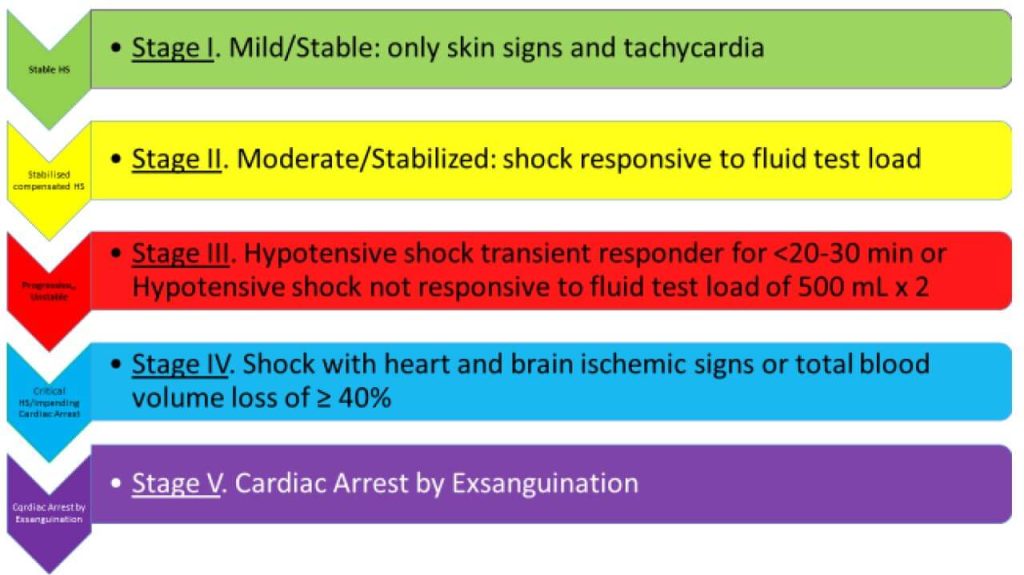
Acute lung injury and post-cardiac arrest syndrome: a narrative review
Abstract Background Post-cardiac arrest syndrome (PCAS) presents a multifaceted challenge in clinical practice, characterized by severe neurological injury and high mortality rates despite advancements in management strategies. One of the important critical aspects of PCAS is post-arrest lung injury (PALI), which significantly contributes to poor outcomes. PALI arises from a complex interplay of pathophysiological mechanisms, […]
Acute lung injury and post-cardiac arrest syndrome: a narrative review Read Post »