Assessment of recruitment from CT to the bedside: challenges and future directions
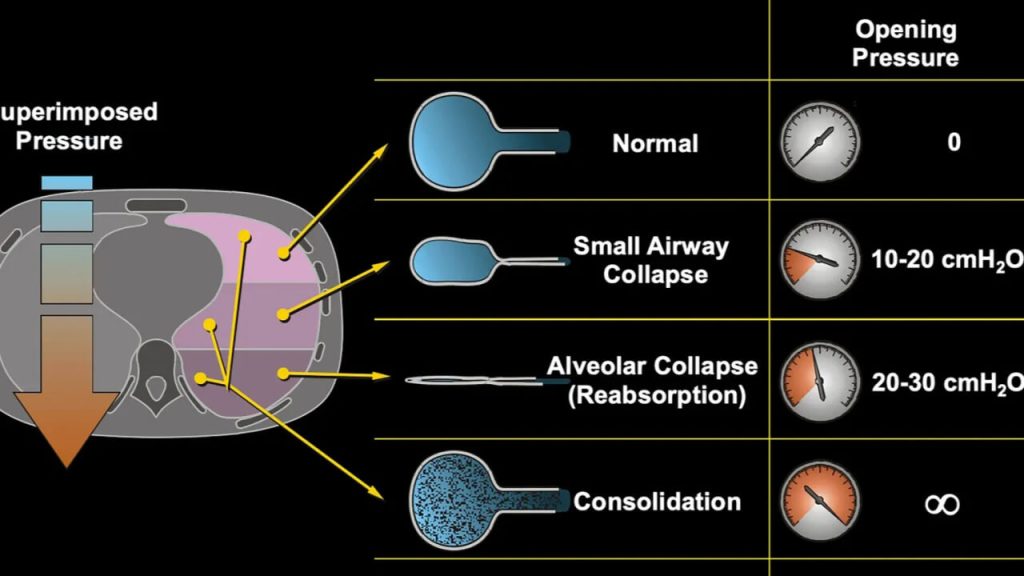
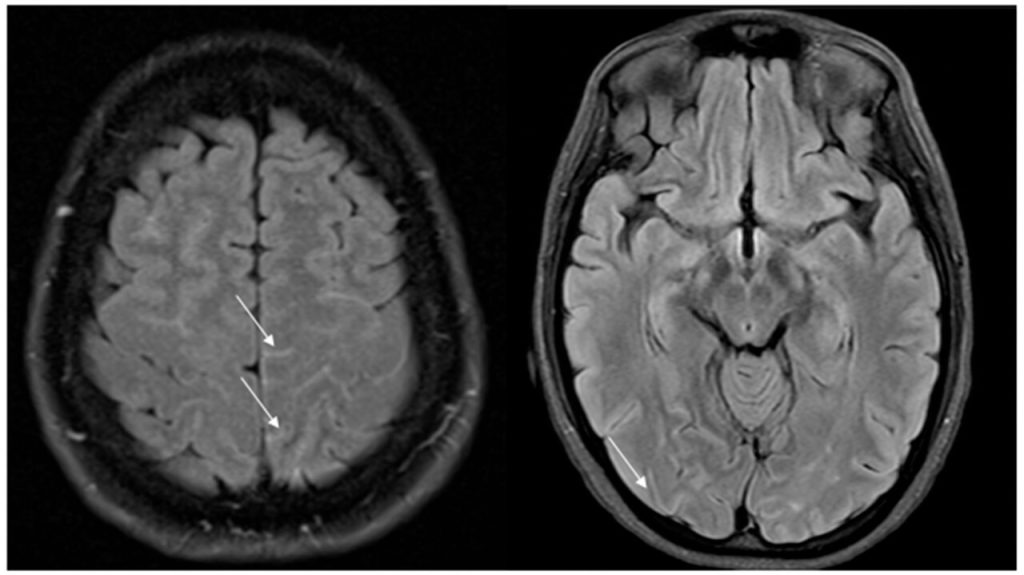
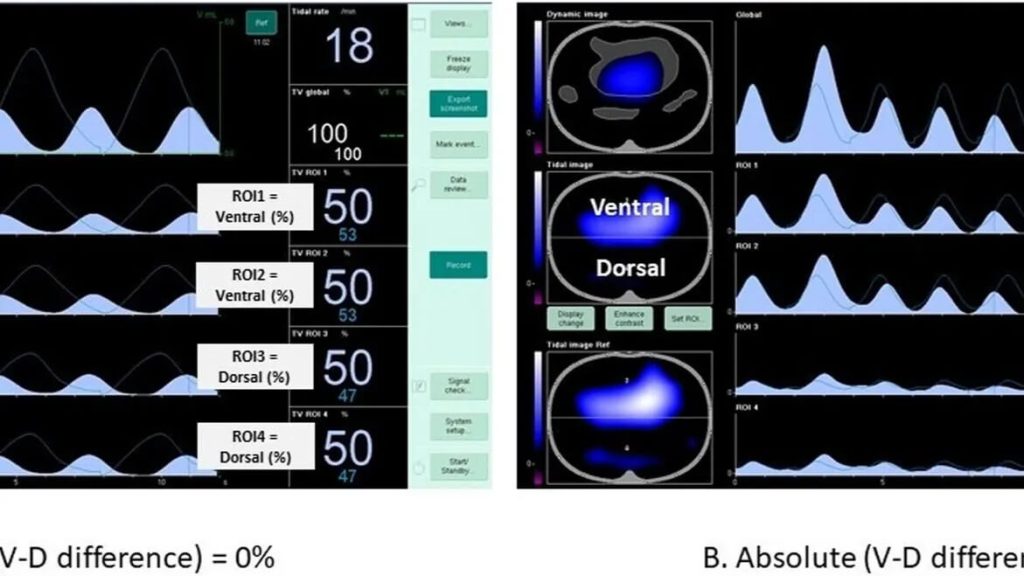
Abstract Assessing and quantifying recruitability are important for characterizing ARDS severity and for reducing or preventing the atelectrauma caused by the cyclic opening and closing of pulmonary units. Over the years, several methods for recruitment assessment have been developed, grouped into three main approaches: 1) Quantitative CT Scanning: This method accurately measures the amount of […]
Assessment of recruitment from CT to the bedside: challenges and future directions Read Post »