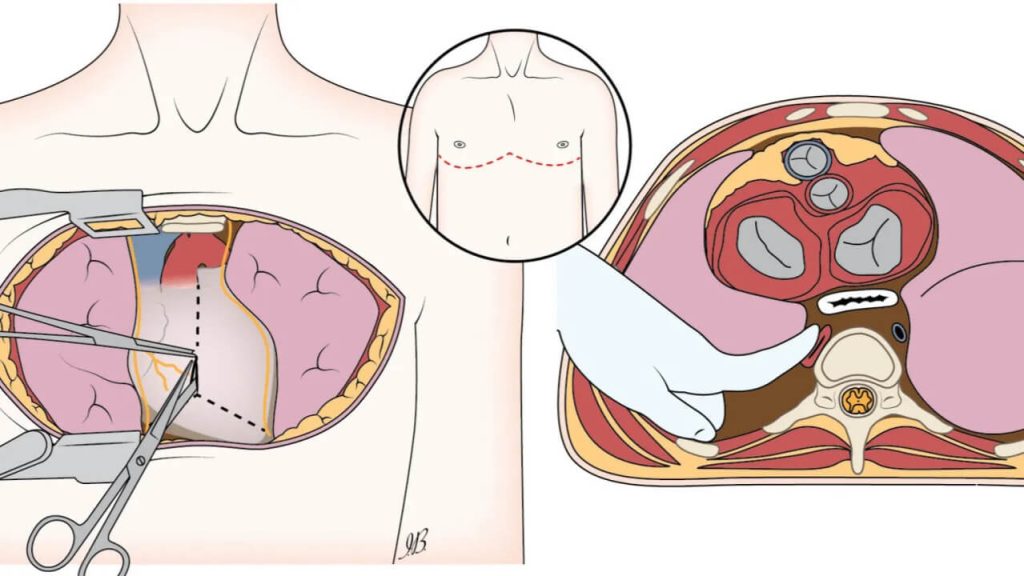
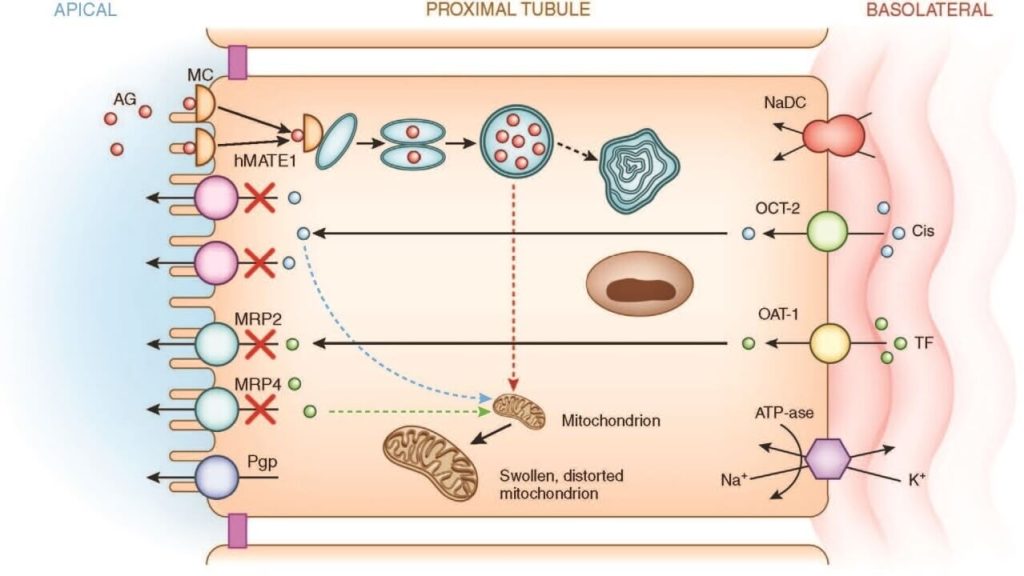
Contemporary management of traumatic cardiac arrest and peri-arrest states: a narrative review
Abstract Trauma is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide across all age groups, with traumatic cardiac arrest (TCA) presenting a significant economic and societal burden due to the loss of productive life years. Despite TCA’s high mortality rate, recent evidence indicates that survival with good and moderate neurological recovery is possible. Successful resuscitation […]