Awake vs. Sedated Cannulation for Extra-Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Patients with COVID-19 Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
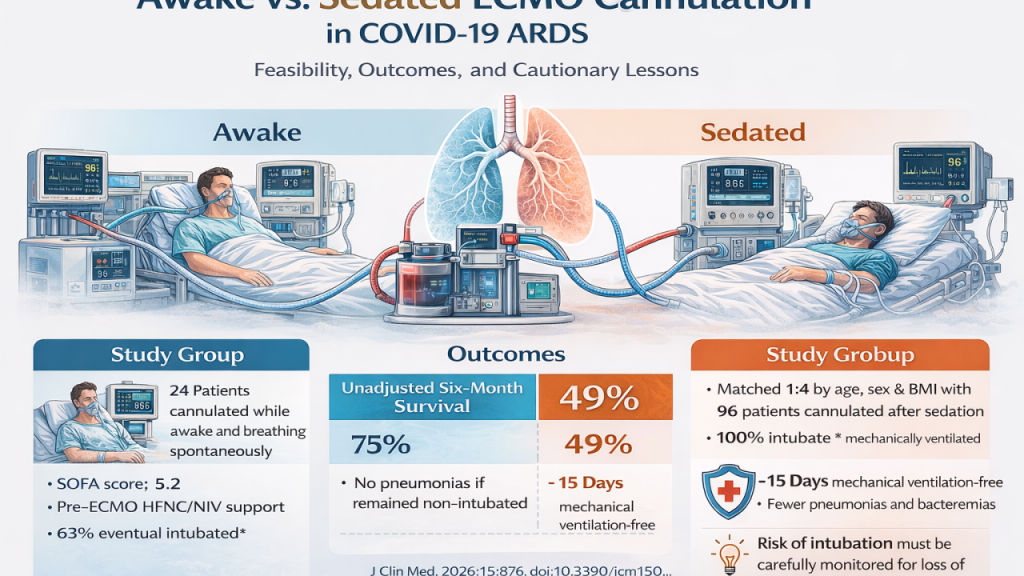
Why this article matters Veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV-ECMO) is routinely initiated in patients with severe ARDS after intubation, deep sedation, and often neuromuscular blockade. During the COVID-19 pandemic, however, some centers explored an alternative strategy: awake ECMO cannulation, in which patients are cannulated while spontaneously breathing and supported without invasive mechanical ventilation. The […]