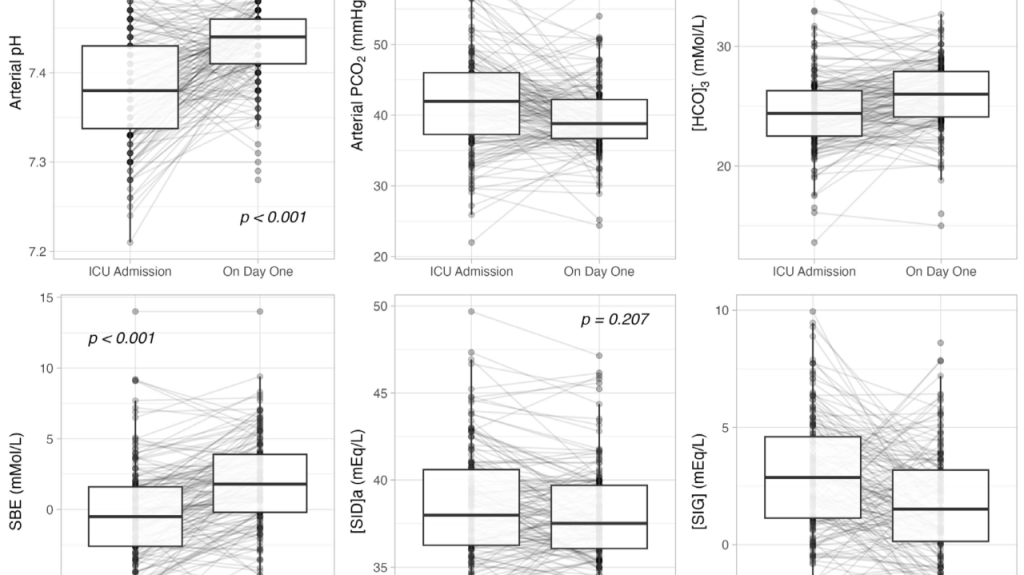
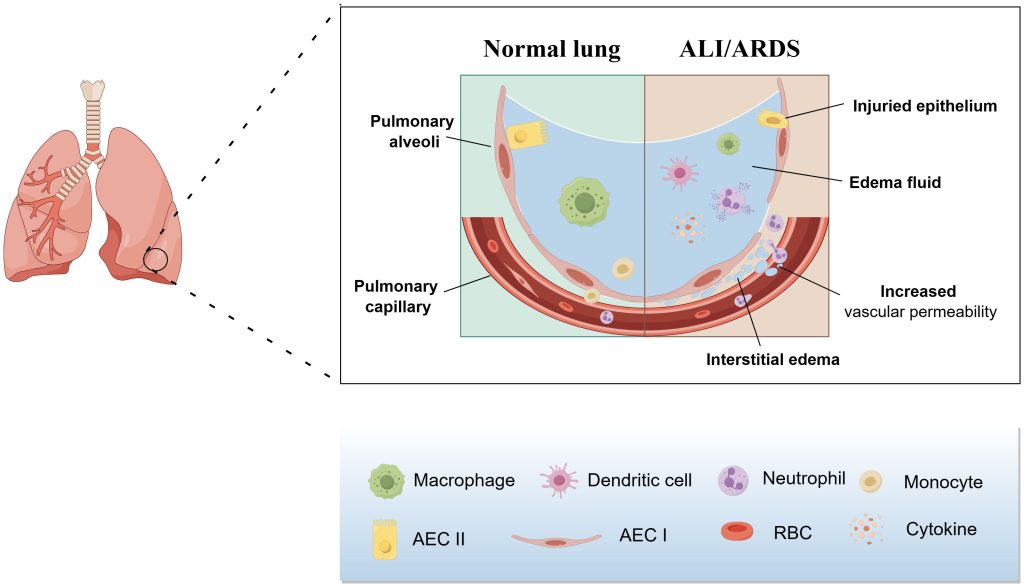
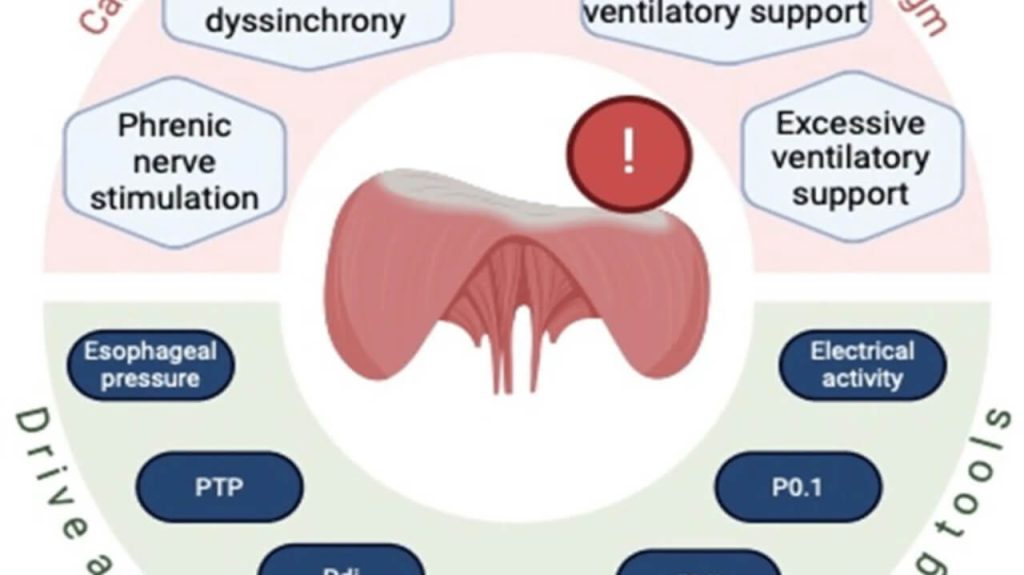
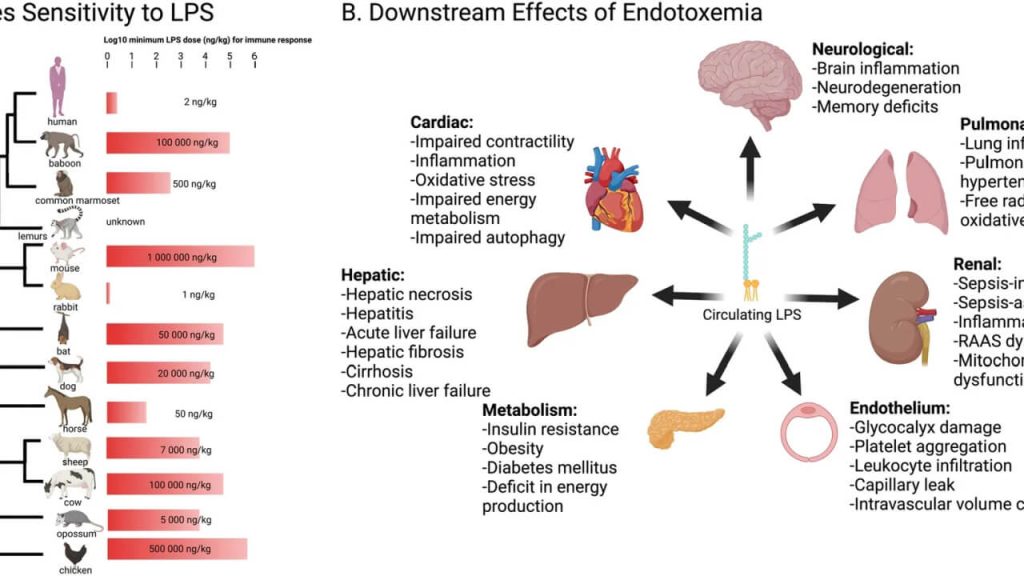
Demystifying Volume Status
Summary Accurate evaluation of patient volume status is crucial yet challenging, impacting critical decisions on fluid management and vasoactive therapies. Traditional clinical methods often lack precision due to complexities in fluid distribution and homeostasis. This review provides a structured physiologic framework leveraging point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) to assess volume status comprehensively. It emphasizes integrating central venous […]
Demystifying Volume Status Read Post »