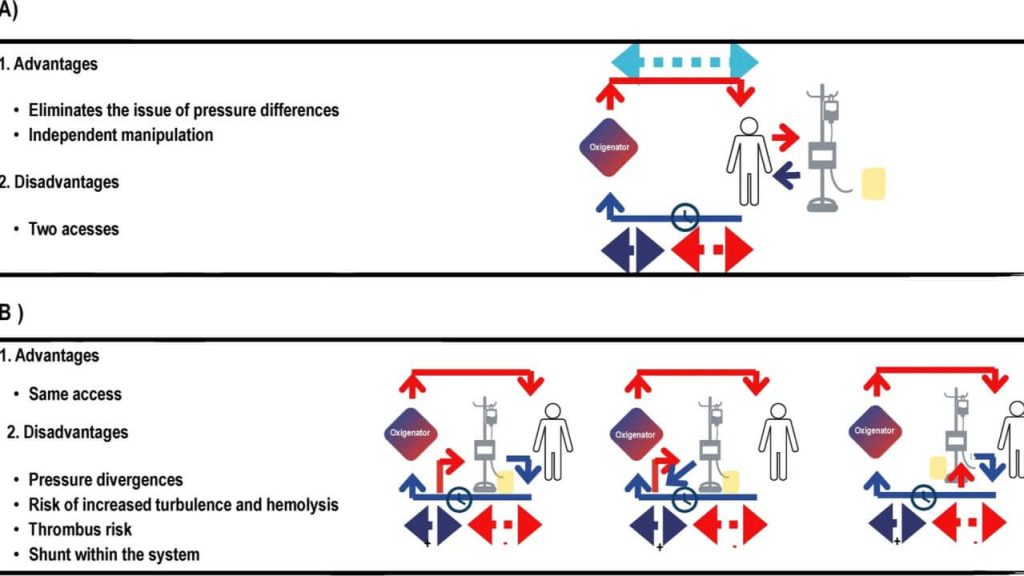
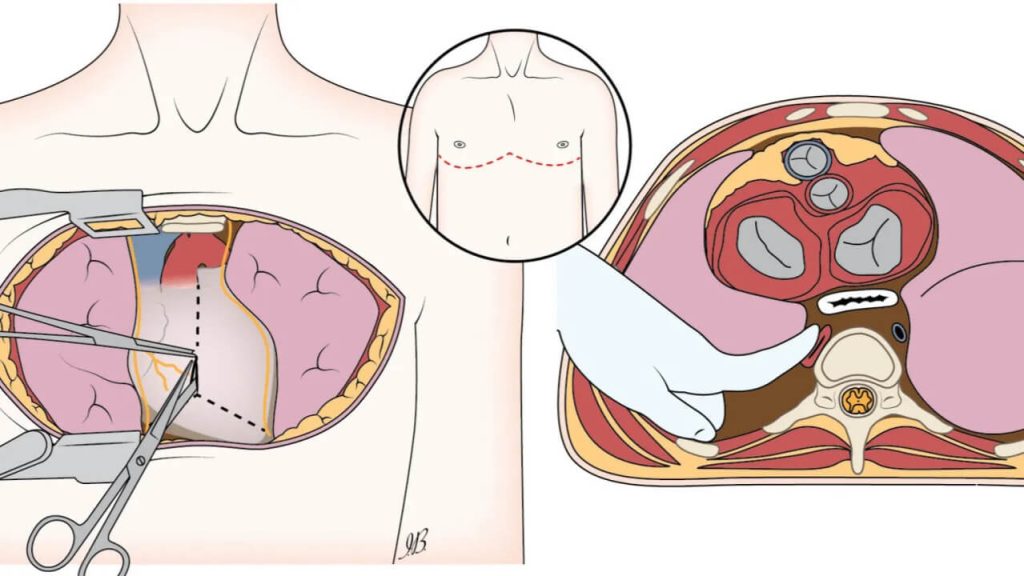
Advancements in understanding the mechanisms of lung–kidney crosstalk
Abstract This narrative review delves into the intricate interplay between the lungs and the kidneys, with a focus on elucidating the pathogenesis of diseases influenced by immunological factors, acid–base regulation, and blood gas disturbances, as well as assessing the effects of various therapeutic modalities on these interactions. Key disorders, such as anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) […]
Advancements in understanding the mechanisms of lung–kidney crosstalk Read Post »