Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: mitochondria and energy metabolism
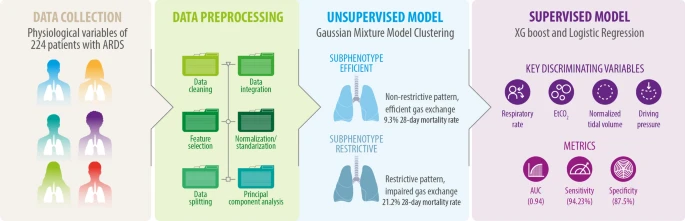
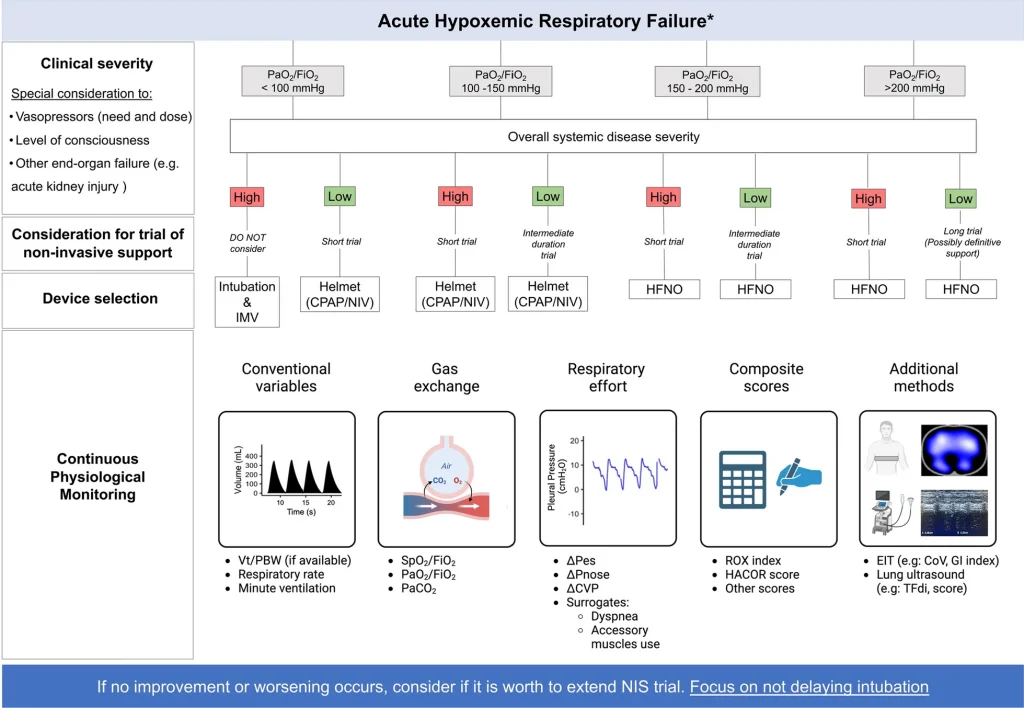
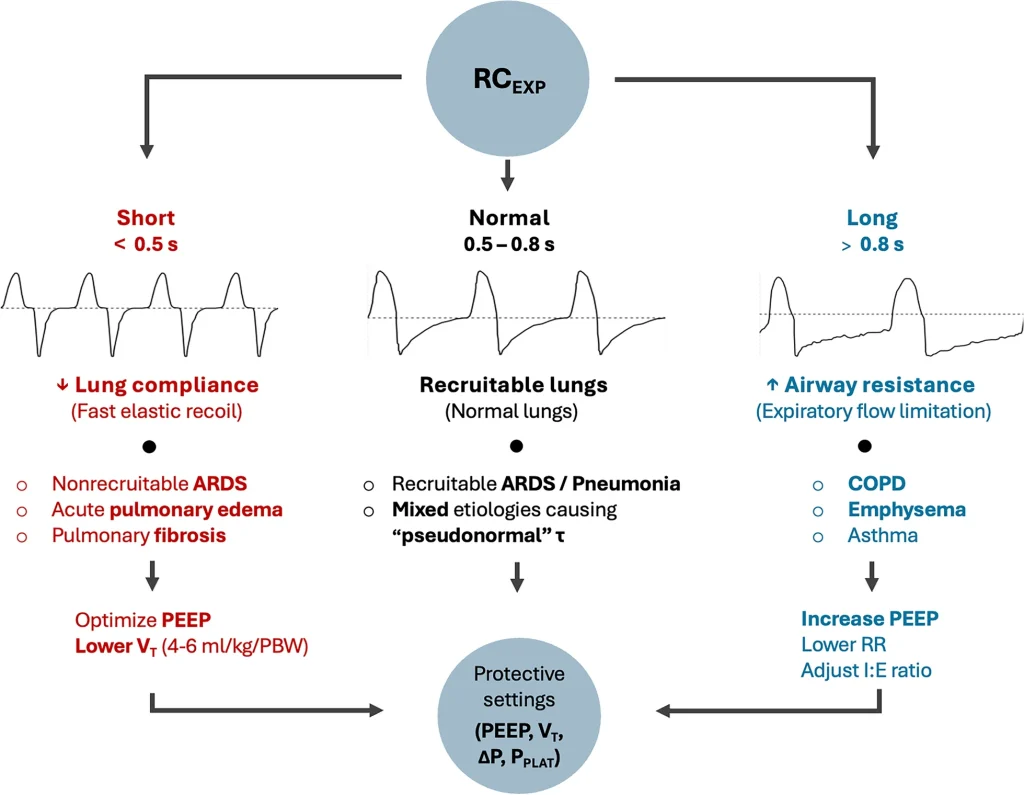
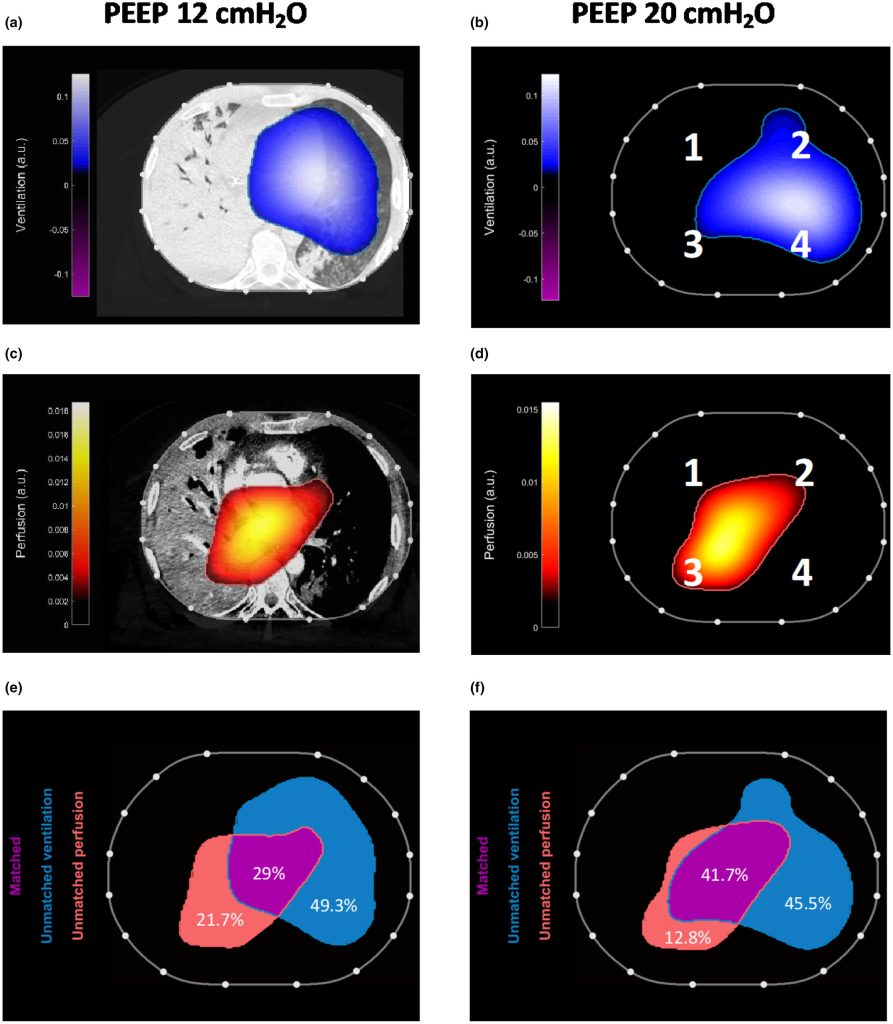
Summary of Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: mitochondria and energy metabolism (Yu et al.) Abstract Summary: Yu et al. systematically reviewed the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction (SIMD), emphasizing mitochondrial dysfunction and disruptions in myocardial energy metabolism. The review highlights critical aspects, including alterations in myocardial substrates, mitochondrial damage, oxidative stress, calcium imbalance, mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) […]
Sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction: mitochondria and energy metabolism Read Post »