Practical approach to thrombocytopenia in patients with sepsis: a narrative review
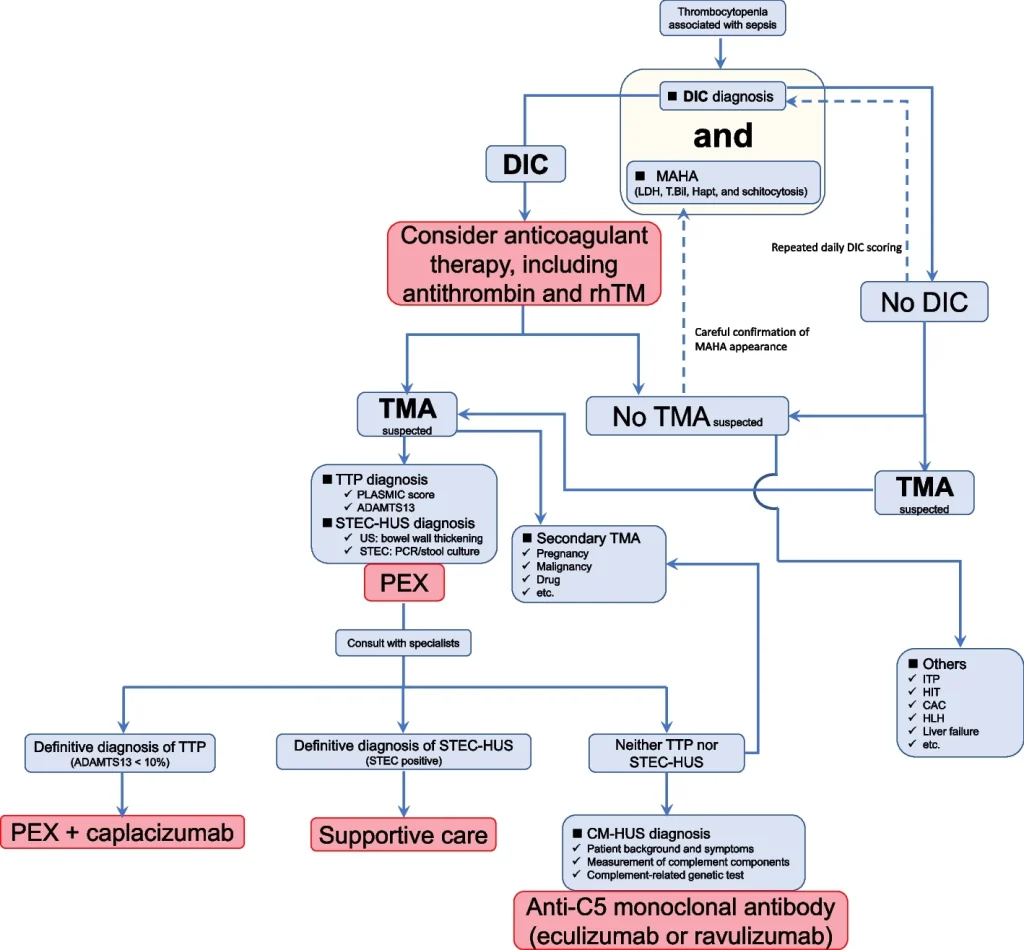
Summary of Practical approach to thrombocytopenia in patients with sepsis: a narrative review Abstract: Thrombocytopenia is common in sepsis, with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) being a frequent cause, though thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA)—including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)—is increasingly recognized. Differentiating DIC from TMA is challenging due to overlapping clinical and laboratory […]
Practical approach to thrombocytopenia in patients with sepsis: a narrative review Read Post »