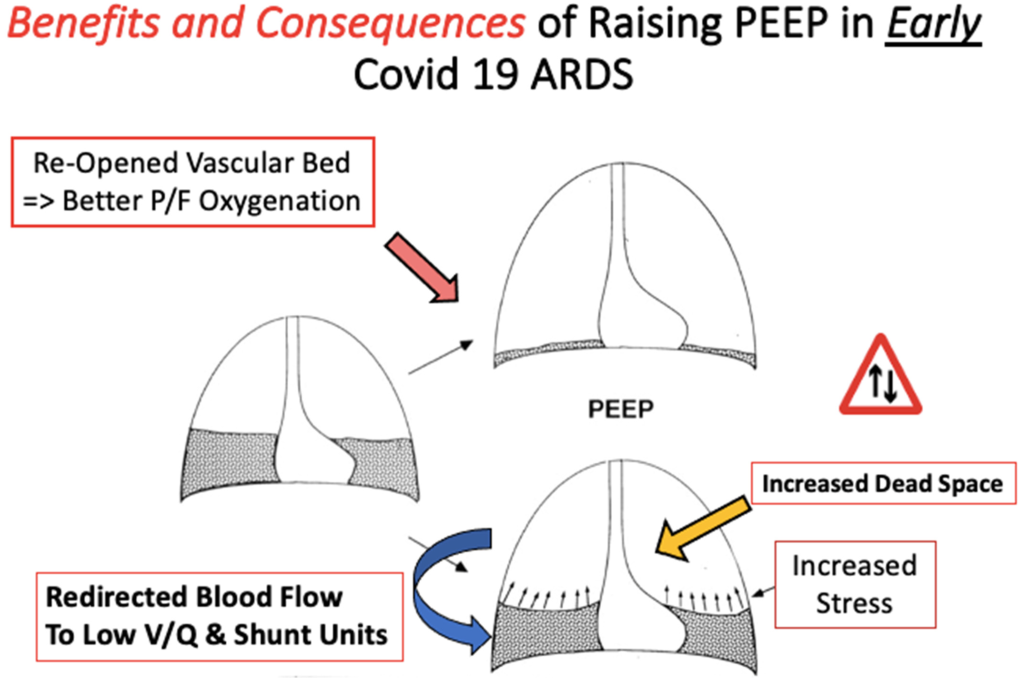
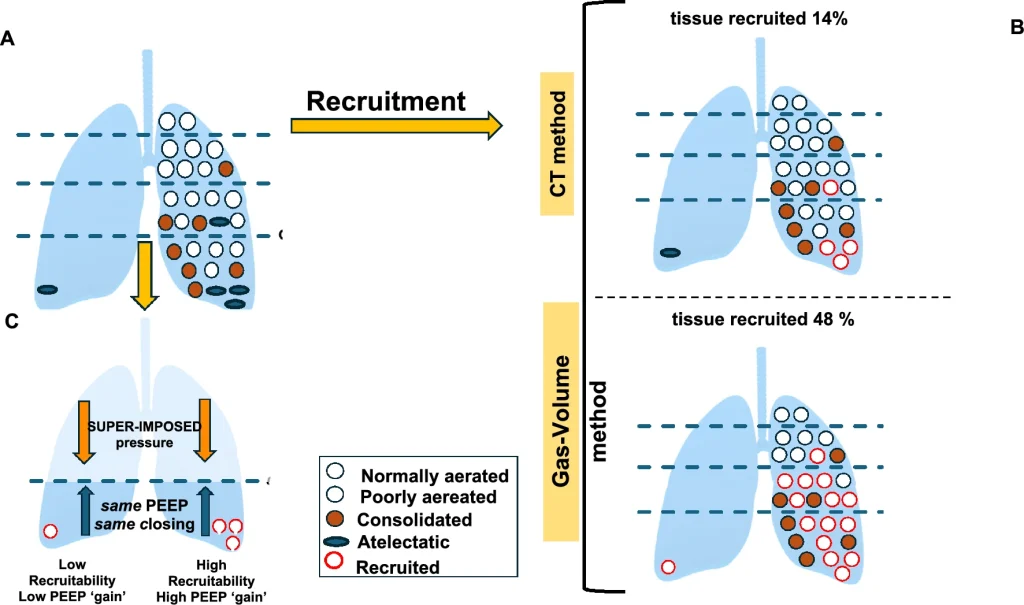
Post-Traumatic Cerebral Infarction: A Narrative Review of Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Abstract Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a common diagnosis requiring acute hospitalization. Long-term, TBI is a significant source of health and socioeconomic impact in the United States and globally. The goal of clinicians who manage TBI is to prevent secondary brain injury. In this population, post-traumatic cerebral infarction (PTCI) acutely after TBI is an important […]