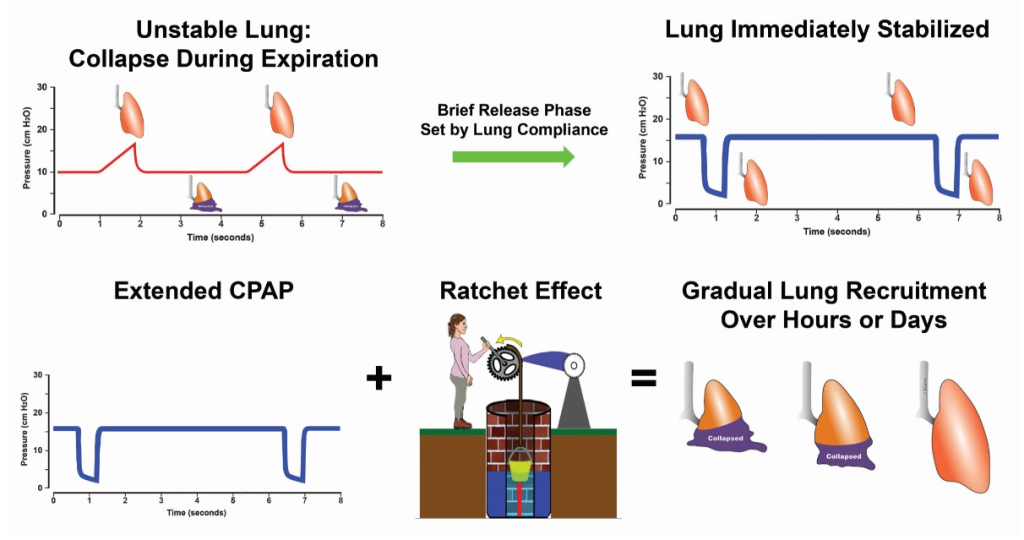
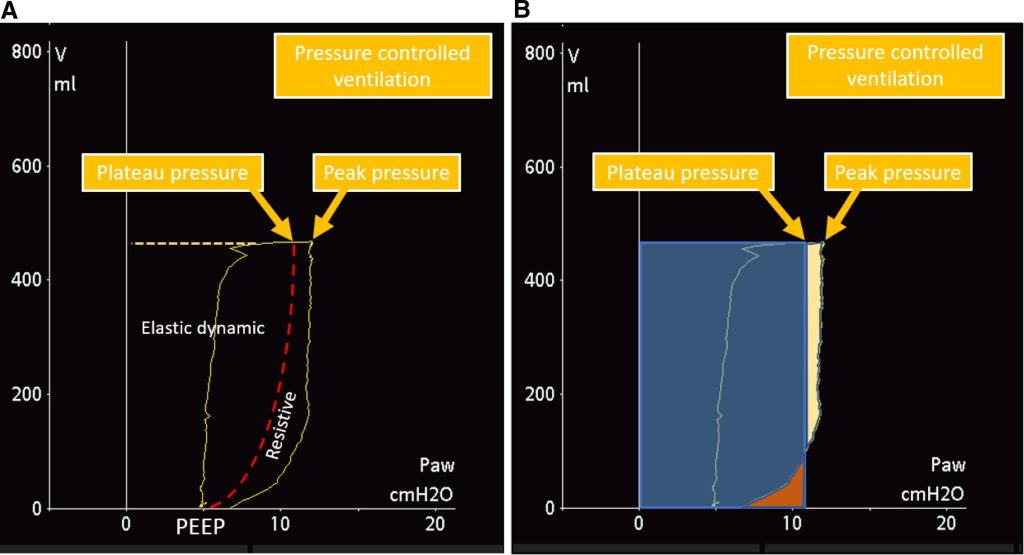
Revisiting Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ventilation management: Time for a paradigm shift focusing on tidal volume
Abstract: Merola and colleagues critically evaluate current Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) ventilation strategies, emphasizing limitations inherent in universally applying low tidal volume (VT) strategies. They argue for personalized, physiology-driven ventilation approaches that incorporate mechanical power, compliance, and transpulmonary pressures. The authors highlight the complexity and heterogeneity of ARDS, suggesting the inadequacy of global parameters […]