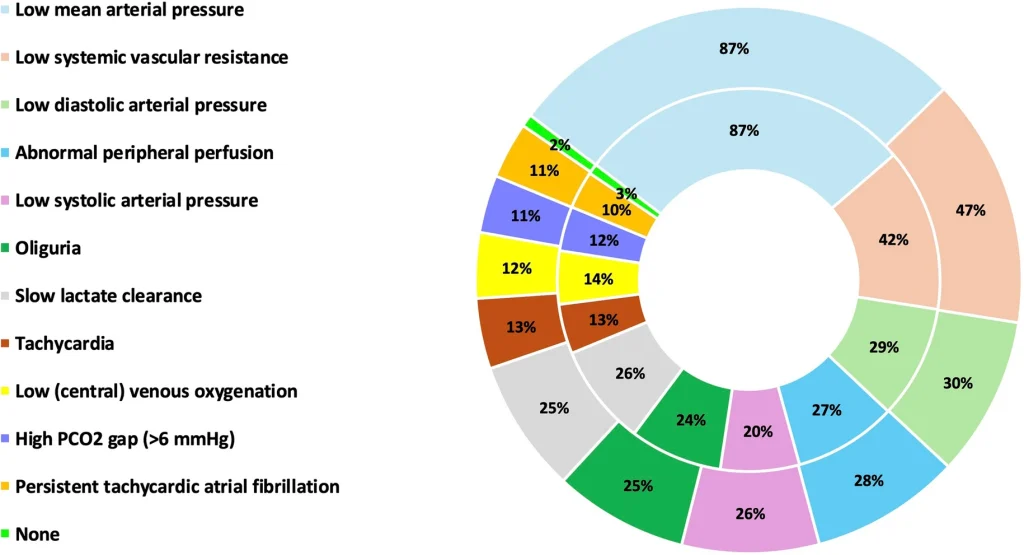
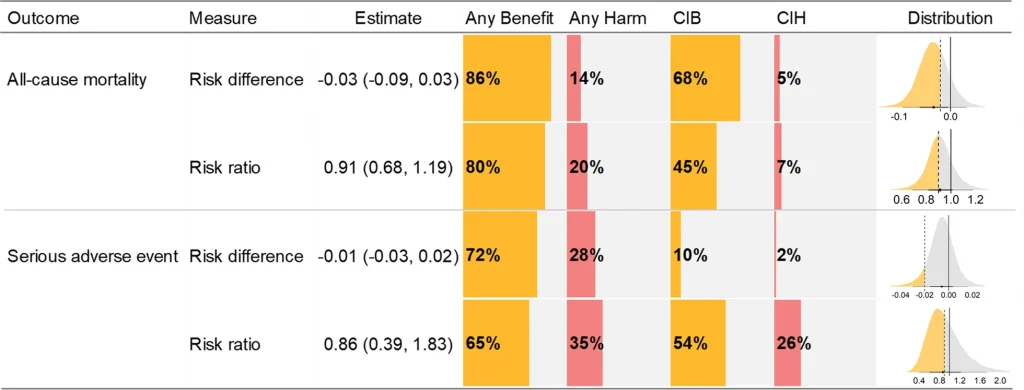
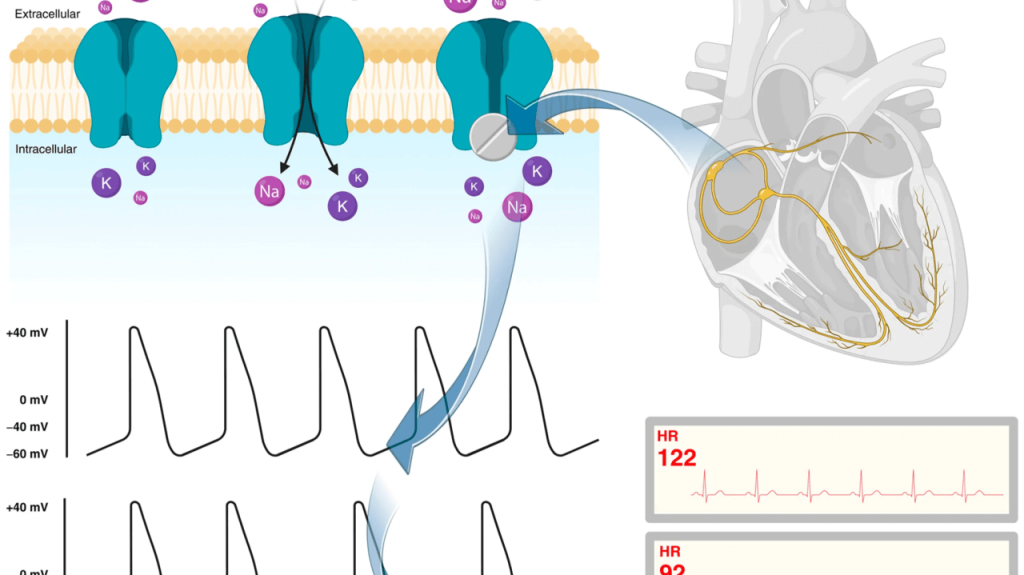
Vasopressin use across shock states: international insights from an international ESICM-endorsed survey: the PRESS Survey
Summary This international survey, endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM), assessed the current clinical use of vasopressin and terlipressin in patients with septic shock. The survey included 1,919 intensivists from 124 countries, highlighting significant variability in vasopressin availability, clinical indications, dosing strategies, and discontinuation practices. Results underscore the heterogeneity of current […]