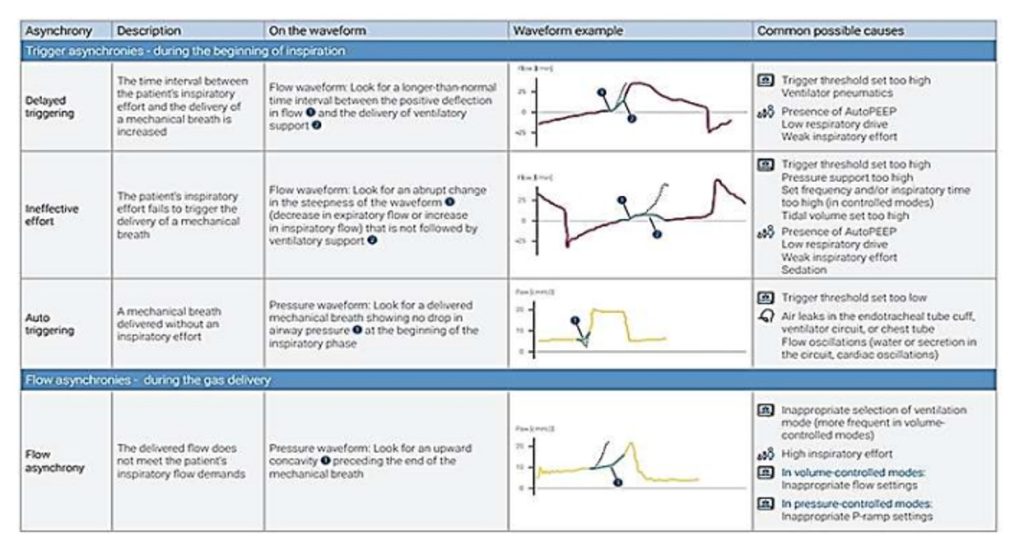
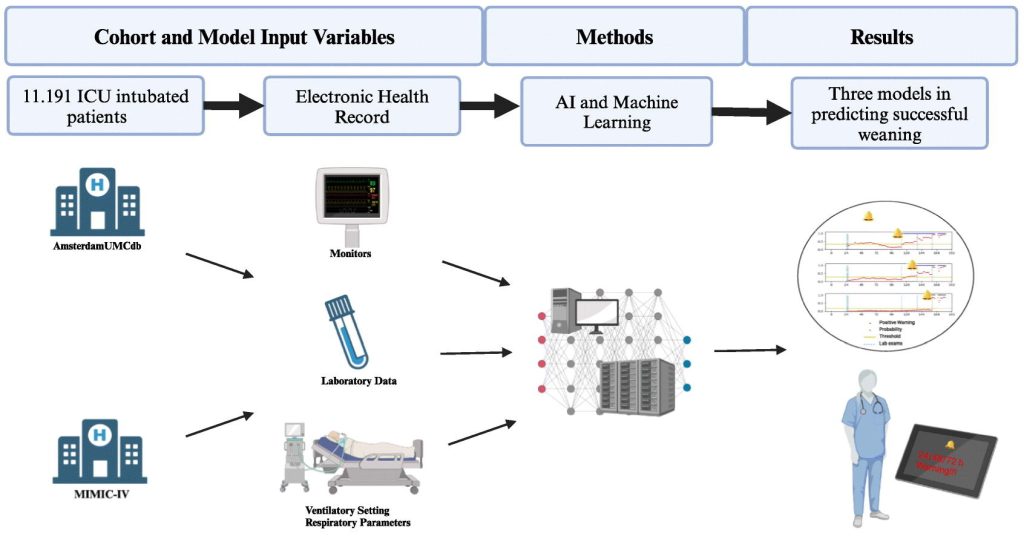
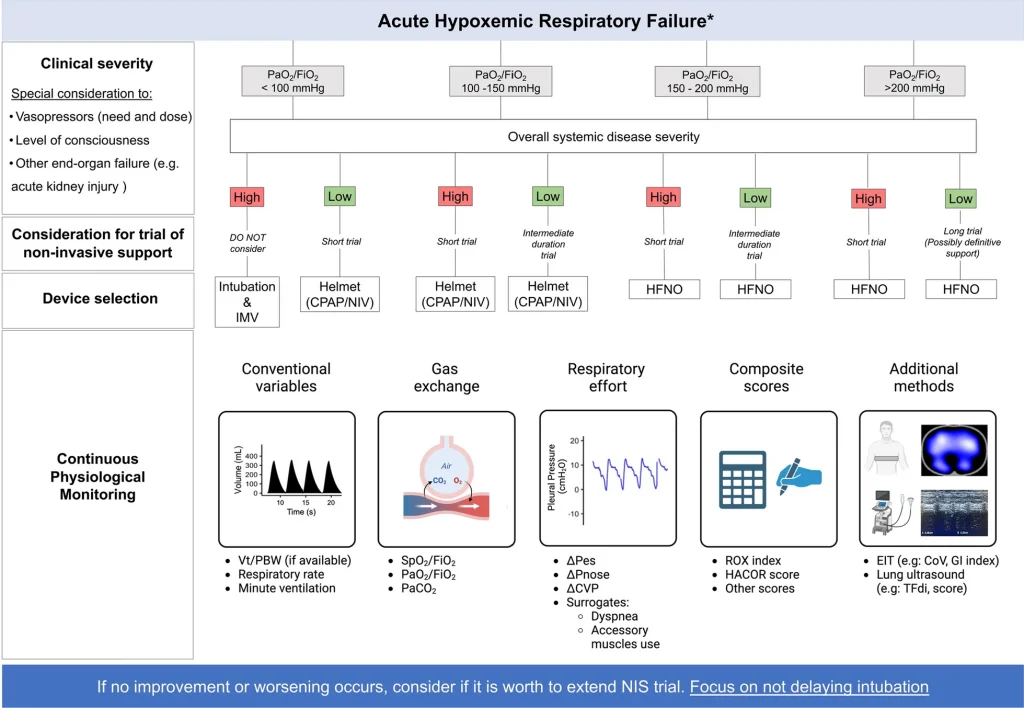
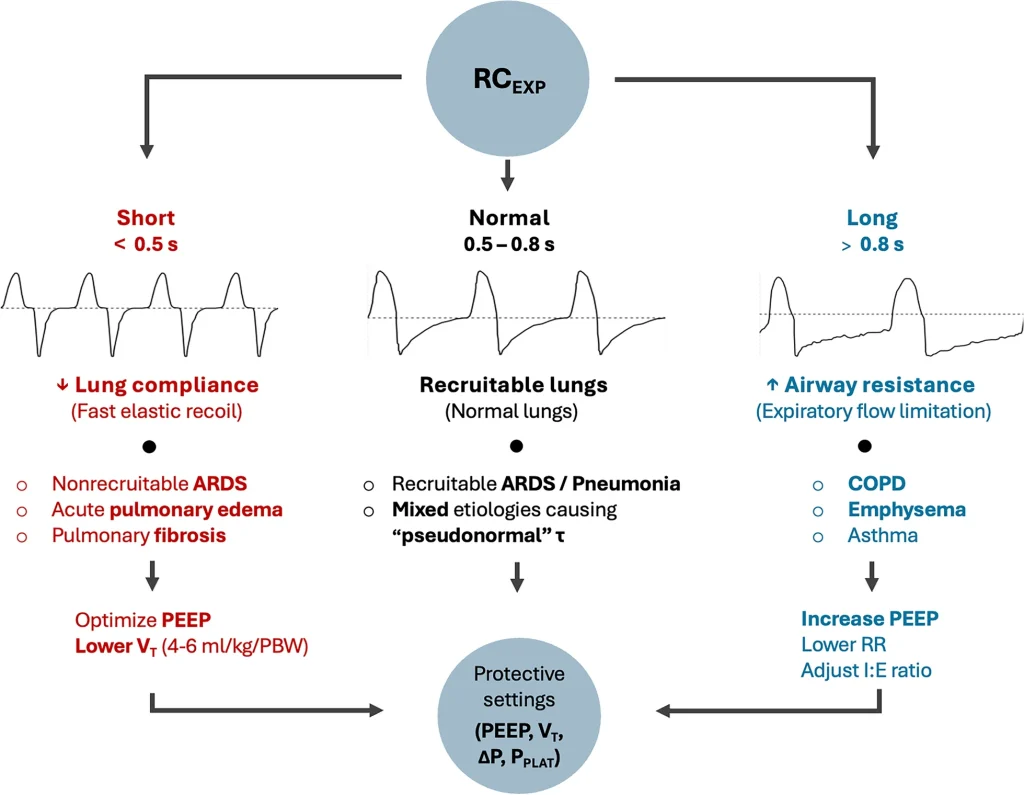
Bedside Assessment of the Respiratory System During Invasive Mechanical Ventilation
Summary The article provides an in-depth review of bedside methods for assessing respiratory mechanics in patients receiving invasive mechanical ventilation. It emphasizes physiological principles guiding clinical management and differentiates between extensive and intensive ventilatory parameters. Detailed methods for evaluating passive patients and those making spontaneous respiratory efforts are outlined, aiming to minimize ventilator-induced lung injury […]
Bedside Assessment of the Respiratory System During Invasive Mechanical Ventilation Read Post »