Prognostic implication of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in acute myocardial infarction-related cardiogenic shock
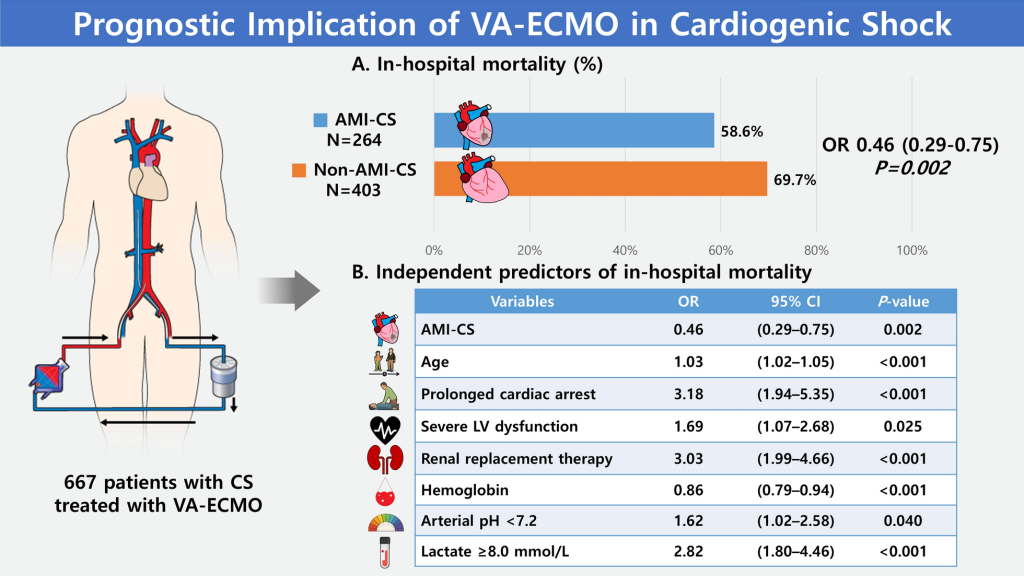
Summary This retrospective study aimed to evaluate clinical outcomes in patients receiving veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) for cardiogenic shock (CS), comparing acute myocardial infarction-related cardiogenic shock (AMI-CS) with non-AMI-CS. Analysis of data from 667 patients treated between 2008 and 2023 showed that AMI-CS was associated with significantly lower in-hospital mortality compared to non-AMI-CS. Independent […]