1. Introduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) leads to pronounced hemodilution and provokes a systemic inflammatory response from blood interaction with artificial surfaces (Ziyaeifard et al., 2014) (, ). Ultrafiltration (UF) mitigates these effects..
Read MoreIntroduction Hemophilia is a hereditary bleeding disorder caused by deficiency of clotting factor VIII (Hemophilia A) or factor IX (Hemophilia B), resulting in impaired blood coagulation and a heightened risk..
Read More1. Introduction Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a chronic, inherited blood disorder resulting from a single point mutation in the β-globin gene. This mutation leads to the production of hemoglobin..
Read MoreIn modern cardiac surgery, cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) plays a life-saving role. It allows the heart to be stopped safely while the body is perfused with oxygenated blood. However, it’s a..
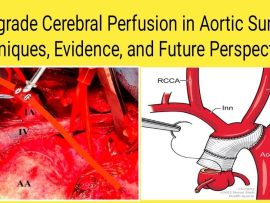
Read More1. Introduction Cerebral protection is a cornerstone of successful aortic arch surgery, where the brain is highly vulnerable during periods of circulatory arrest. While deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA) alone..
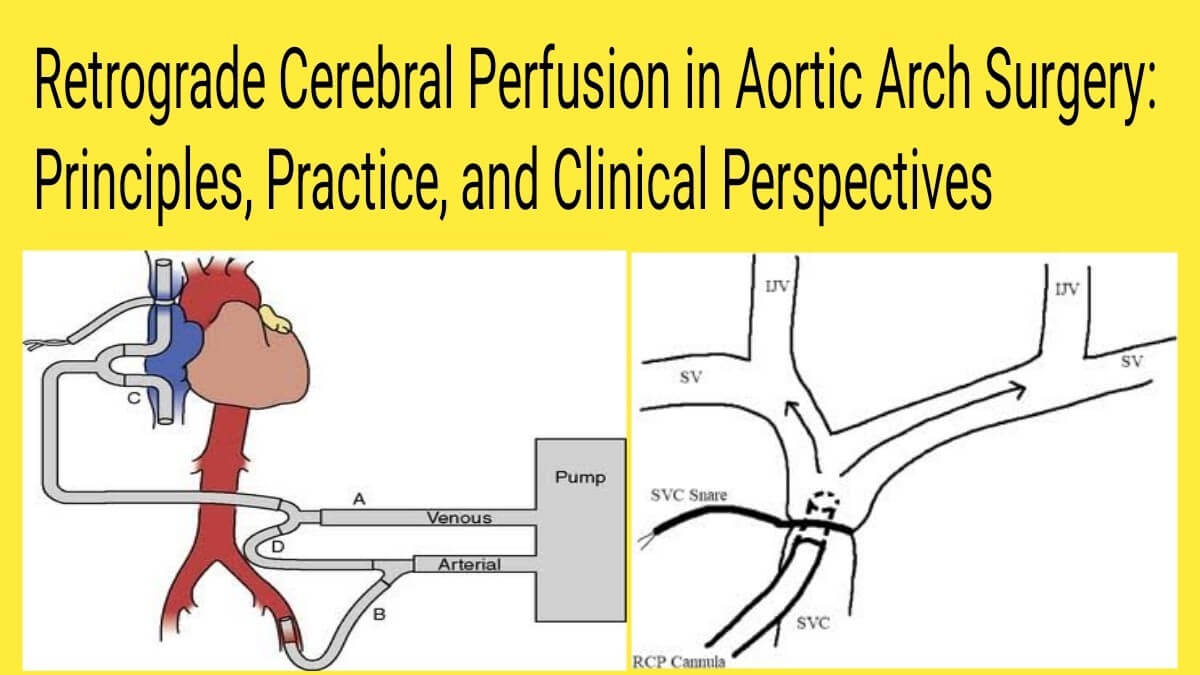
Read More1. Introduction Aortic arch surgery presents significant neurologic risks due to the potential for cerebral ischemia during circulatory arrest. Traditional methods such as deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA) provided limited..
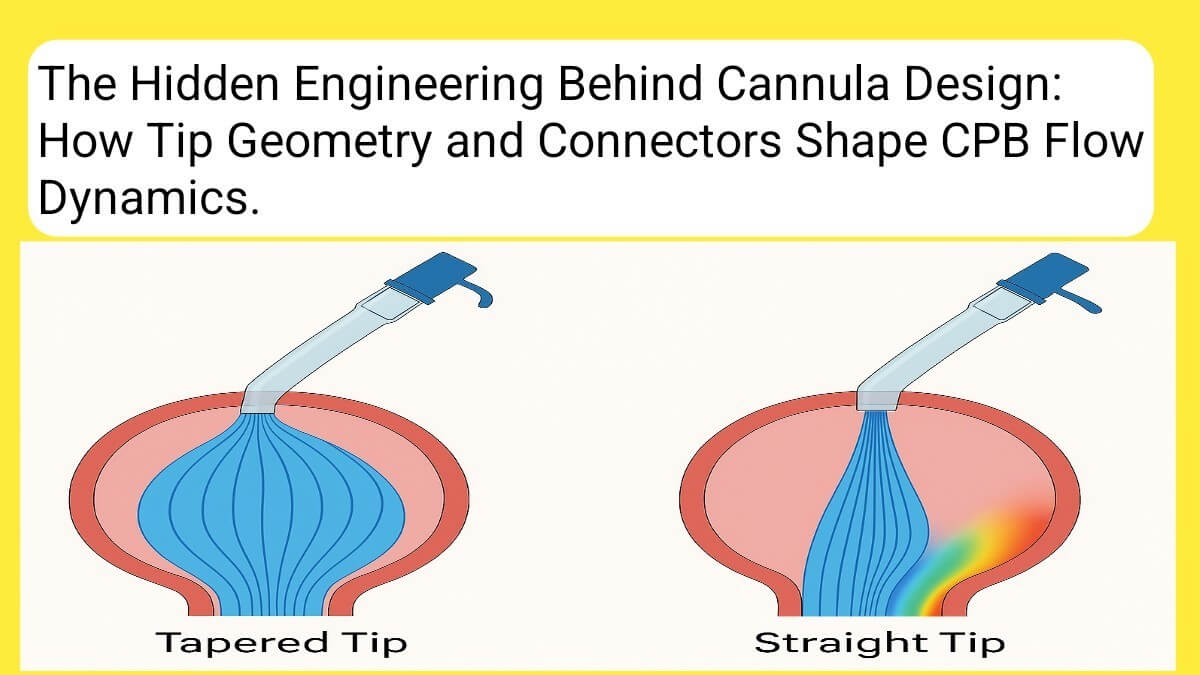
Read MoreIntroduction: More Than Just a Tube In the world of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), the arterial cannula is far more than a simple conduit for blood flow. Every feature—from the shape..
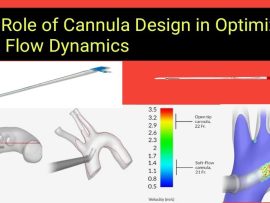
Read MoreIn the complex world of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), where precision, safety, and efficiency govern every aspect of patient care, the significance of flow dynamics cannot be overstated. While the primary..
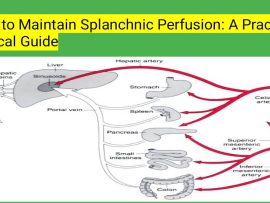
Read MoreIntroduction Splanchnic perfusion refers to the blood flow through the splanchnic circulation, which supplies the gastrointestinal organs including the stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, and spleen. Maintaining adequate splanchnic blood flow..
Read MoreIntroduction The heart is nature’s pulsatile pump, delivering rhythmic surges of blood critical not only for oxygen transport but also for maintaining vascular health. Cardiopulmonary bypass, a lifesaving intervention, often..
Read MoreIn cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), roller and centrifugal pumps have been the mainstays for decades, each with unique benefits and challenges. However, these traditional blood pumps come with inherent pressure-related risks..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is fundamental to modern cardiac surgery, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures on a still and bloodless heart. However, traditional CPB systems are associated with complications..
Read MoreIntroduction Myocardial protection during cardiac surgery is a critical determinant of patient outcomes. Traditional cardioplegia techniques primarily aim to arrest the heart, reduce metabolic demand, and preserve myocardial viability (Buckberg,..
Read MoreIntroduction: Cardiopulmonary bypass, a cornerstone of modern cardiac surgery, temporarily diverts blood away from the heart and lungs, allowing for surgical intervention in a controlled environment. During CPB, blood is..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is essential for modern cardiac surgery, allowing complex repairs and reconstructions by diverting blood away from the heart and lungs. However, during this process, the heart's..
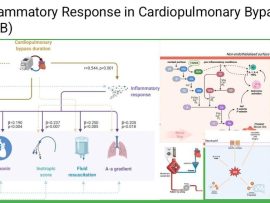
Read MoreAbstract: Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) induces a multifactorial systemic inflammatory response that significantly contributes to postoperative complications such as acute lung injury, renal dysfunction, and increased morbidity. This response is initiated..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) has revolutionized cardiac surgery by temporarily taking over the function of the heart and lungs during complex procedures. Central to this technique is the management of..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) plays a pivotal role in modern cardiac surgery by temporarily assuming the functions of the heart and lungs during complex procedures. However, despite its life-saving capabilities,..
Read MoreIntroduction: Cardiac surgery is among the most delicate and high-risk procedures in modern medicine, and the use of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is central to its success. In this complex setting,..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a cornerstone of modern cardiac surgery, facilitating complex intracardiac procedures by temporarily assuming the function of the heart and lungs. One of the most critical..
Read MoreCardiopulmonary Bypass (CPB) is one of the most critical advancements in cardiac surgery. It allows the surgical team to operate on a non-beating heart by temporarily taking over the functions..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) has long been a cornerstone of cardiac surgery. However, conventional CPB circuits are associated with a range of physiological disturbances including hemodilution, inflammatory response, and coagulopathy...
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiac surgery is a highly specialized and complex field that requires the seamless coordination of multiple professionals, each bringing their expertise to ensure a successful outcome. The success of..
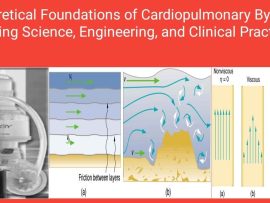
Read MoreIntroduction: A Heart That Pauses, A Circuit That Lives When the heart is arrested during cardiac surgery, life continues—thanks to cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). The theoretical underpinnings of CPB stem from..
Read MoreAbstract Perfusionists are central to life-sustaining interventions such as cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and mechanical circulatory support. While the technical dimensions of their work are well recognized,..
Read MoreIntroduction Oxygen is vital to life and a central element of cardiopulmonary support. During cardiac surgery—whether on mechanical ventilation or cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB)—100% oxygen is often used out of tradition..
Read MoreAbstract This case report discusses a rare and critical perfusion accident during a minimally invasive coronary artery bypass grafting (CAGB) procedure, where a Eurosets Skipper oxygenator burst 3 minutes after..
Read MoreAbstract Background: Management of arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO₂) during extracorporeal circulation is critical to maintaining physiological stability. Both cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) significantly alter natural..
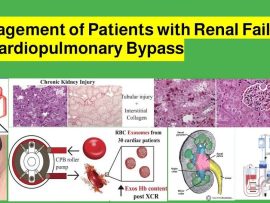
Read MoreAbstract Renal failure presents a significant challenge in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), as they are at high risk for acute kidney injury (AKI), electrolyte imbalances, and fluid overload. The..
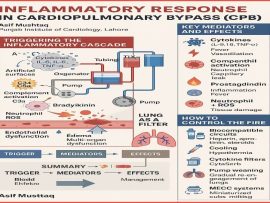
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a life-saving technology used in cardiac surgery; however, it triggers a systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) due to blood contact with non-endothelial surfaces, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and..
Read More