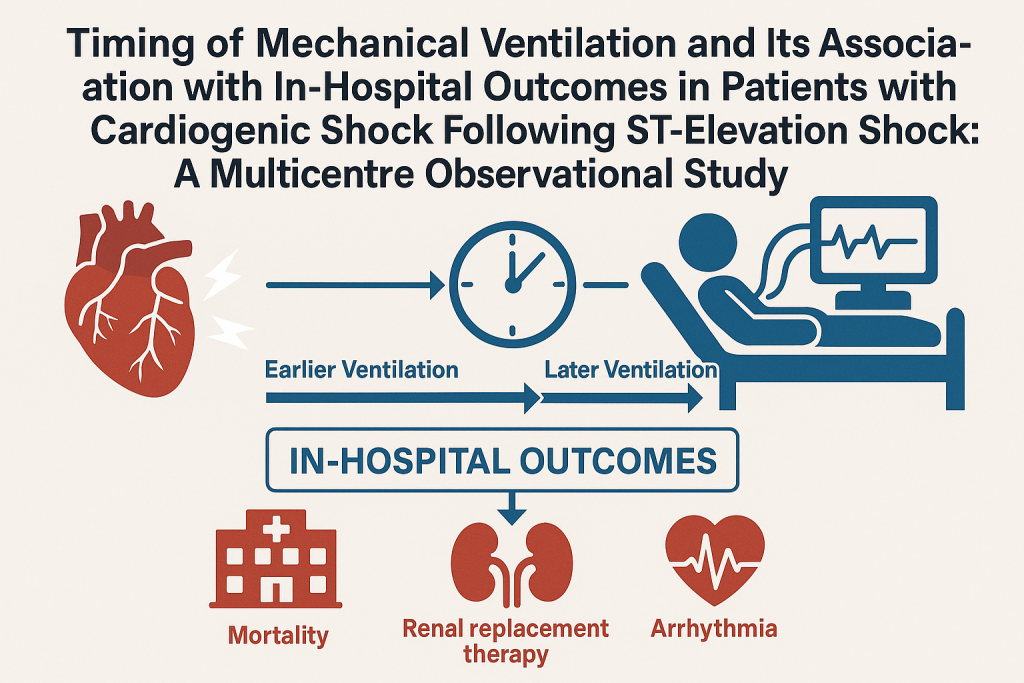
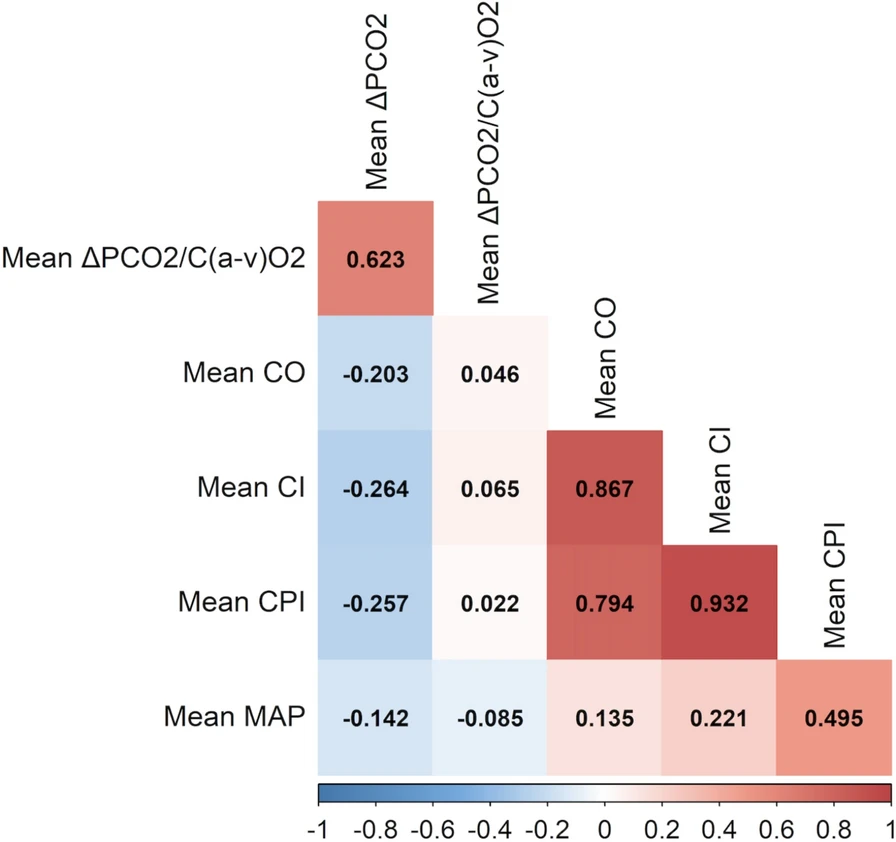
Management of cardiogenic shock: state-of-the-art
Abstract: Jung et al. provide a comprehensive review addressing current knowledge and contemporary practices in the management of cardiogenic shock (CS). Despite advancements, mortality remains high, and the complexity of patient care underscores the need for individualized treatments. The authors highlight recent evidence in pharmacological therapies, mechanical circulatory support (MCS), and the potential for personalized […]
Management of cardiogenic shock: state-of-the-art Read Post »