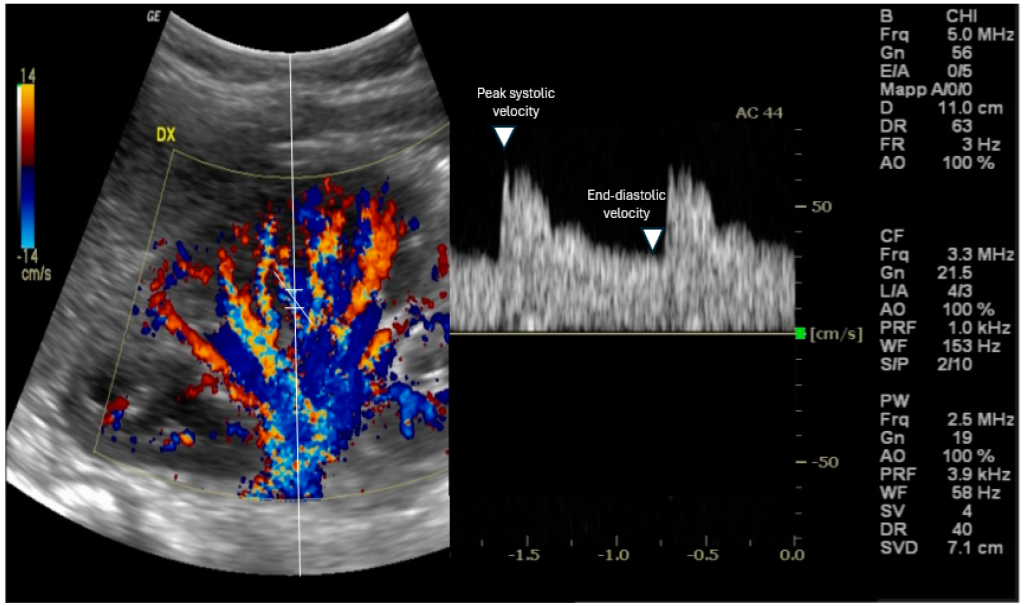
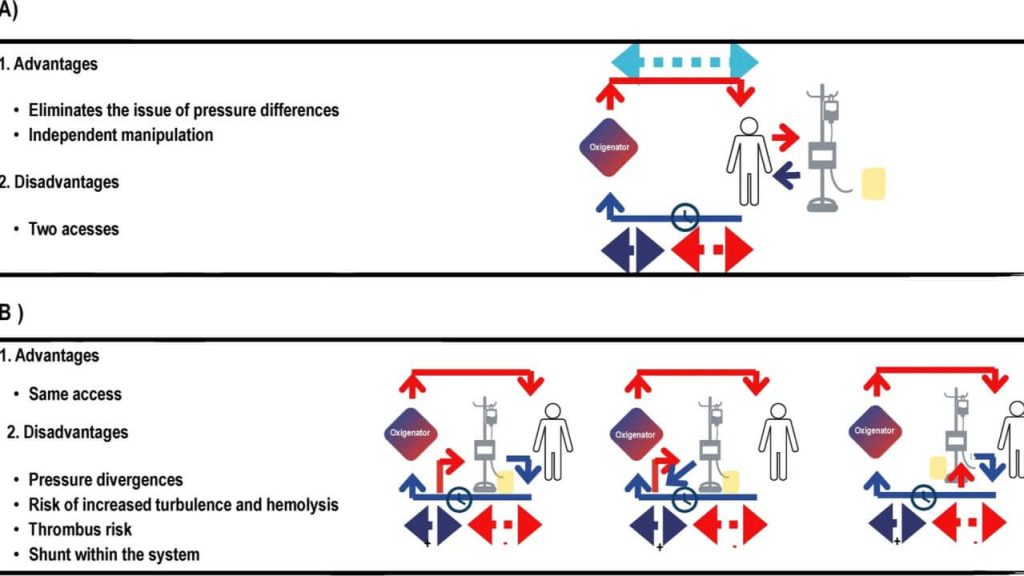
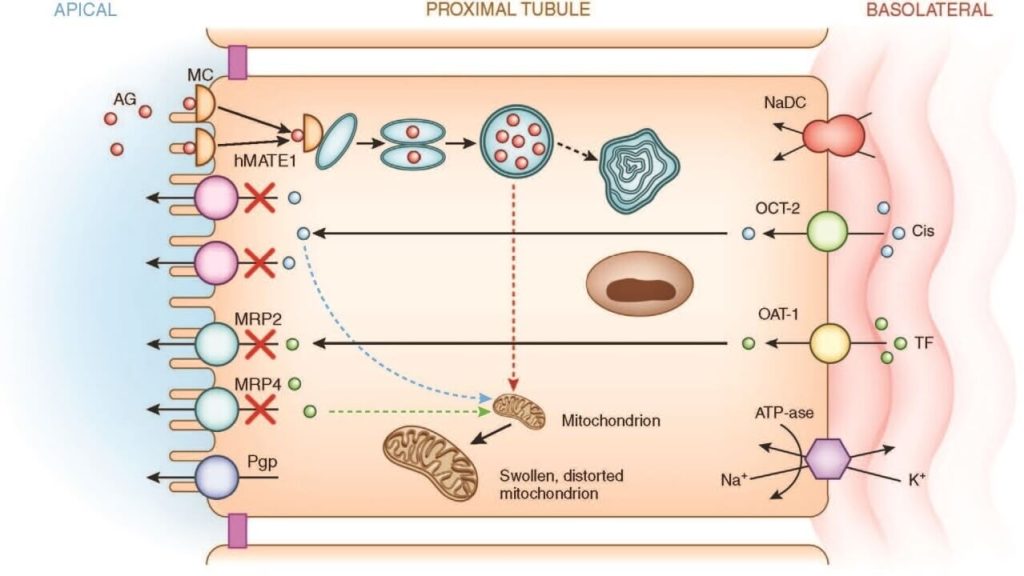
Exploring the Utility of Renal Resistive Index in Critical Care: Insights into ARDS and Cardiac Failure
Summary of “Exploring the Utility of Renal Resistive Index in Critical Care: Insights into ARDS and Cardiac Failure” Abstract The renal resistive index (RRI), a Doppler ultrasound-derived metric, offers a non-invasive window into renal hemodynamics, especially relevant in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and heart failure (HF). This narrative review explores RRI’s physiological […]