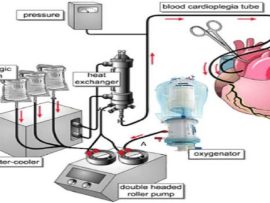
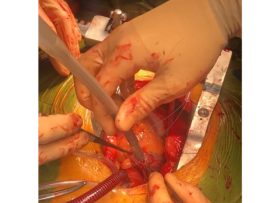
Minimally invasive mitral valve repair (MICS) with neochords combines a precise surgical technique with an advanced perfusion strategy to optimize outcomes. The minimally invasive approach can be performed routinely, delivering..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a cornerstone of modern cardiac surgery, facilitating a bloodless and motionless field for surgeons. Traditionally, hyperoxia—elevated levels of arterial oxygen tension (PaO₂)—has been employed during..
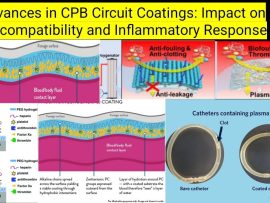
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a lifesaving technology in cardiac surgery, but it introduces blood-material interactions that trigger inflammatory and coagulative responses. To address these issues, advancements in biocompatible CPB..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) has transformed cardiac surgery, allowing for safe and controlled procedures on the arrested heart. However, a long-standing debate in perfusion science is whether CPB should be..
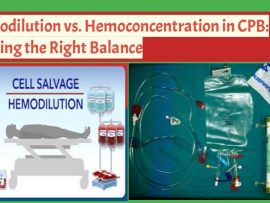
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) introduces significant alterations in blood composition due to the priming solution, fluid shifts, and extracorporeal circulation. Hemodilution and hemoconcentration represent two opposing strategies, each with distinct..
Read MoreIntroduction Extracorporeal circulation (ECC), used in cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), serves as a temporary replacement for the heart and lungs. It maintains tissue perfusion and gas..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) has been the cornerstone of modern cardiac surgery, allowing for safe cardiac arrest while maintaining systemic perfusion. However, the debate between pulsatile and non-pulsatile flow during..
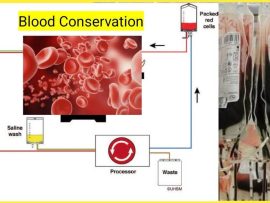
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a vital component of cardiac surgery, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures on a still, bloodless heart. However, CPB is associated with significant hemodilution, coagulopathy,..
Read MoreLeft ventricular outflow tract obstruction in neonates and infants encompasses a variety of anatomical defects, ranging from isolated aortic valve stenosis or discrete subaortic stenosis to the more complex tunnel..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is essential in cardiac surgery, but high-risk patients—such as pediatric, geriatric, and renal-compromised individuals—require specialized priming strategies to optimize outcomes. A one-size-fits-all approach can lead to..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a critical component of cardiac surgery, allowing the heart to be temporarily stopped while maintaining circulation and oxygenation. Proper hemodynamic management during CPB is essential..
Read MoreIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a life-saving technology that temporarily replaces the heart and lungs during cardiac surgery. The choice of priming solution plays a crucial role in maintaining hemodynamic..
Read More1. Introduction Cardioplegia plays a crucial role in myocardial protection during cardiac surgery by inducing controlled cardiac arrest and minimizing ischemic injury. Over the years, various cardioplegia strategies have evolved,..
Read MoreIntroduction Isolated Limb Perfusion (ILP) is a targeted chemotherapy technique used primarily for treating locally advanced limb malignancies, such as soft tissue sarcomas and melanoma. By isolating the limb’s vascular..
Read MoreIntroduction Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) is an advanced oncologic perfusion technique designed to treat peritoneal carcinomatosis, a condition where cancer spreads within the peritoneal cavity (Sugarbaker, 1995). This innovative approach..
Read MoreLeft Heart Bypass: An Overview Introduction Left Heart Bypass (LHB) is a surgical technique used to temporarily divert blood from the left side of the heart to maintain distal perfusion..
Read MoreIntroduction The history of cardiac surgery in Pakistan is often credited to various institutions, but a lesser-known and largely undocumented fact is that the first open-heart surgery in Pakistan was..
Read MoreCardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a cornerstone of modern cardiac surgery, enabling complex procedures by temporarily taking over the heart and lung functions. However, one of the most critical aspects of..
Read MoreIntroduction The European Board of Cardiovascular Perfusion (EBCP) establishes standardized guidelines to ensure quality and safety in perfusion practices across Europe. These guidelines provide a framework for clinical protocols, training,..
Read MoreSerum lactate is a critical biomarker in cardiac surgery, offering insights into tissue oxygenation and metabolic status. Elevated lactate levels during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) can indicate inadequate perfusion, hypoxia, or..
Read MoreIntroduction Blood gas management during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is crucial for optimizing oxygen delivery and cerebral perfusion, especially in temperature-regulated surgeries such as deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA). Two primary..
Read MorePerfusionists play a critical role in cardiac surgery and extracorporeal support, ensuring optimal oxygenation and circulation during procedures. However, given the complexity of the field, even experienced professionals can make..
Read MoreCardioplegia is a pharmacological therapy administered during cardiac surgery to intentionally and temporarily arrest the heart. The first solution used during cardiopulmonary bypass was reported by Dr. Melrose in the..
Read MoreTechnical Aspects of Cardiopulmonary Bypass Process Overview Blood is drained from the vena caval filters directly into a reservoir. Normally a single two-stage cannula is used (drains blood from the..
Read MoreAn arterial cannula is usually inserted into the ascending aorta. Alternate sites include the femoral, innominate or axillary artery in situations such as emergency, redo surgery, minimally invasive surgery or..
Read More