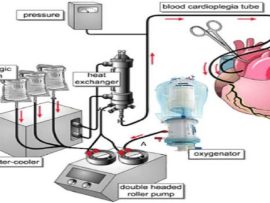
Abstract Background Cardiopulmonary bypass is widely used in cardiac surgery but often leads to lung ischemia–reperfusion injury, a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Despite advances in critical care, effective..
Read MoreAbstract Remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPreC) has been regarded as a promising strategy to reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury to the heart and other organs caused by cardiopulmonary bypass. While RIPreC has demonstrated..
Read MoreAbstract Organ preservation plays a critical role in addressing transplantation challenges, including donor shortages and ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). Continuous advancements in preservation technologies are essential to meet the increasing demand..
Read MoreAbstract OBJECTIVES Although lung transplantation has experienced great development in the past decades, the survival rate remains low, and lung ischaemia–reperfusion injury during transplantation is a major cause of primary..
Read MoreAbstract Brain injury and cerebral inflammation are frequent complications following cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) resulting in neurocognitive dysfunction, encephalopathy, or stroke. We compared cerebral inflammation induced by del Nido and histidine-tryptophan-α-ketoglutarate..
Read More1. Introduction Cardioplegia plays a crucial role in myocardial protection during cardiac surgery by inducing controlled cardiac arrest and minimizing ischemic injury. Over the years, various cardioplegia strategies have evolved,..
Read MoreAbstract Background/Objectives: Previously, we showed that blood-based polarizing cardioplegia exerted beneficial cardioprotection during hypothermic ischemia; however, these positive effects of blood-based polarizing cardioplegia were reduced during normothermic ischemia compared to..
Read MoreAbstract Background and Objectives: The majority of cardiac surgical procedures are performed using cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia-induced cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest and reperfusion may lead to ischemia-reperfusion injury of the..
Read MoreLevels of Circulating Ketone Bodies in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery on Cardiopulmonary Bypass
Abstract Ketone bodies (KBs) are energy-efficient substrates utilized by the heart depending on its metabolic demand and substrate availability. Levels of circulating KBs have been shown to be elevated in..
Read MoreAbstract Cardiac surgery, including surgical aortic valve repair (SAVR) and coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), are associated with ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. Single bouts of exercise, including handgrip exercise, may protect..
Read MoreAbstract Objectives Ischemia–reperfusion injury often coincides with a , which can result in following . Our previous research has demonstrated improvement by cytokine adsorption during ex vivo lung perfusion. The aim of this study was..
Read MoreAbstract This review presents an integrated approach to the analysis of myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury and the modulating influence of myocardial conditioning during the evolution of acute myocardial infarction..
Read MoreAbstract An essential procedure for the treatment of myocardial infarction is restoration of blood flow in the obstructed infarct artery, which may cause ischaemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Heart I/R injury manifests..
Read MoreAbstract Purpose Historically, cardiac surgery patients have often been managed with supraphysiologic intraoperative oxygen levels to protect against the risks of cellular hypoxia inherent in the un-physiologic nature of surgery..
Read More