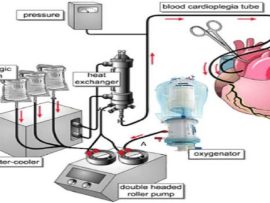
Abstract Background Cardioplegia is delivered via antegrade, retrograde, or combined perfusion routes. Antegrade cardioplegia follows the physiological path but may be less effective in patients with severe coronary disease. Retrograde..
Read MorePRO Cardioplegia, the intentional and temporary arrest of the heart during cardiac surgery, has been a cornerstone of modern heart transplantation, enabling myocardial protection during ischemic periods. Its use dates..
Read MoreAbstract Objectives After cardiac surgery, long aortic clamping times and extracorporeal circulation times are associated with worse outcomes. This study compares hemodynamic performance, myocardial metabolism, and ultrastructural preservation in rat..
Read MoreAbstract Objective To determine if the route of administration of whole blood cardioplegia (cardioplegia) is significantly associated with the frequency of profound transient hypotension (intermittent “vasoplegia”) often observed during cardioplegia..
Read MoreAbstract Objective To compare the utility of a saline-based modified del Nido (mDN) cardioplegia solution with a conventional institutional technique (multidose St. Thomas blood cardioplegia) for mitral valve repair (MVR)..
Read MoreIntroduction Myocardial protection during cardiac surgery is a critical determinant of patient outcomes. Traditional cardioplegia techniques primarily aim to arrest the heart, reduce metabolic demand, and preserve myocardial viability (Buckberg,..
Read More1. Introduction Cardioplegia plays a crucial role in myocardial protection during cardiac surgery by inducing controlled cardiac arrest and minimizing ischemic injury. Over the years, various cardioplegia strategies have evolved,..
Read MoreAbstract Background/Objectives: Previously, we showed that blood-based polarizing cardioplegia exerted beneficial cardioprotection during hypothermic ischemia; however, these positive effects of blood-based polarizing cardioplegia were reduced during normothermic ischemia compared to..
Read MoreAbstract We conducted a high-risk redo mitral valve replacement through a right mini-thoracotomy without rib spreading (redo-MICS MVR) under systemic hyperkalemia combined with circulatory arrest to circumvent complications associated with..
Read MoreAbstract Background: The utility and uptake of Del Nido cardioplegia in adult cardiac surgery is rapidly increasing. Cases with prolonged aortic cross-clamp times necessitate multi-dosing however an understanding of safe..
Read MoreAbstract Aim: We investigated in a single-center retrospective study early outcomes of intermittent warm blood and cold crystalloid St. Thomas cardioplegia in patients referred to CABG due to acute coronary..
Read MoreAbstract Objectives The use of del Nido in adult cardiac surgery is rising in popularity. The objective of this large multicenter study was to evaluate the use and associated outcomes of..
Read MoreAbstract Background and Objectives: The majority of cardiac surgical procedures are performed using cardiopulmonary bypass and cardioplegia-induced cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest and reperfusion may lead to ischemia-reperfusion injury of the..
Read MoreAbstract Background: Histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate (HTK) cardioplegia induces cardiac arrest through membrane hyperpolarization. Aortic valve pathology leads to pathophysiological changes in left ventricular vascularization that may prevent adequate cardioplegic distribution. The objective..
Read MoreAbstract Background St. Thomas cardioplegia is commonly administered to adults, yet repeated dosing at brief intervals is required. Del Nido’s cardioplegic solution provides a prolonged duration of safe myocardial arrest,..
Read MoreAbstract Nowadays, the necessity of having a cardioplegia circuit capable of being adapted in order to administer different types of cardioplegia is strategically fundamental, both for the perfusionist and for..
Read MoreAbstract Myocardial protection and specifically cardioplegia have been extensively investigated in the beginnings of cardiac surgery. After cardiopulmonary bypass had become routine, more and more cardiac operations were possible, requiring..
Read MoreAbstract Purpose The aims of this study were (1) to determine the associations of cardioplegic solutions with postoperative main strong ion difference (mSID), which is the difference between sodium ion..
Read MoreAbstract Introduction Intraoperative myocardial protection during aortic valve replacement (AVR) for aortic stenosis (AS) is of paramount importance for outcomes. The dose of cardioplegia is usually calculated with reference to body mass. Aim..
Read MoreAbstract Antegrade cardioplegia is routinely given during cardiac surgery. The delivery of antegrade cardioplegia from the cardiopulmonary bypass machine has many variables. Many perfusionists rely exclusively on cardioplegia system pressure..
Read MoreAbstract Background The quality of a myocardial protection of a single-dose del Nido cardioplegia versus multiple dose blood-based cardioplegia on myocardial injury, outcomes and operative times in patients undergoing minimally..
Read MoreAbstract Objectives del Nido cardioplegia is utilized for myocardial protection in adult patients undergoing cardiac surgery; however, no standardized re-dosing protocol exists. We describe perfusion characteristics and clinical outcomes in..
Read MoreAbstract The aim of cardiopulmonary bypass is the maintenance of a sufficient whole body perfusion and gas exchange during open or closed heart surgery procedure (coronary artery bypass grafting, valve..
Read MoreAbstract Background Although recently it has been extended for use in adult cardiac surgery, del Nido cardioplegia was originally indicated for pediatric cardiac surgery. In this meta-analysis, we compare del..
Read MoreAbstract Background The efficacy of different cardioplegia solutions on outcomes of complex cardiac operations such as triple valve surgery (TVS) is scarce. Here we compared the outcomes in TVS patients..
Read MoreAbstract Purpose Del Nido cardioplegia (dNC) is a 1:4 formula of blood:crystalloid and contains erythrocytes as oxygen carriers. Hearts donated after circulatory death (DCD) are maintained by ex-vivo machine perfusion..
Read MoreAbstract Open-heart surgery is often an unavoidable option for the treatment of cardiovascular disease and prevention of cardiomyopathy. Cardiopulmonary bypass surgery requires manipulating cardiac contractile function via the perfusion of..
Read MoreAbstract Objectives To compare the safety and efficacy of del-Nido cardioplegia (DNC) with traditional 4:1 cold blood cardioplegia (CBC) in coronary artery bypass grafting and/or valve surgeries in elderly patients...
Read MoreAbstract Objectives Intermittent cold blood cardioplegia is commonly used in children whereas intermittent warm blood cardioplegia is widely used in adults. We aimed to compare clinical and biochemical outcomes with..
Read MoreAbstract Background Myocardial protection during operations with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and aortic cross clamping is vital. For this purpose, Del Nido (DN) and Custodiol cardioplegia (CC) solutions are used for..
Read More