Jörn Tongers, MD, discusses his recently published paper evaluating the efficacy and safety of early combined mechanical circulatory support (MCS) with an Impella® heart pump and venoarterial extracorporeal membrane..
Lee masImpella 5.5 Support beyond 50 Days as Bridge to Heart Transplant in End-Stage Heart Failure Patients
Abstract Prolonged mechanical circulatory support (MCS) for severe left ventricular dysfunction in cardiogenic shock as a bridge to heart transplantation (HTx) generally requires a surgical procedure. Typically, a surgically implanted..
Lee masAbstract The survival rate after cardiac arrest (CA) remains low. The utilization of extracorporeal life support is proposed to improve management. However, this resource-intensive tool is associated with complications and..
Lee masAbstract Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is used in cardiogenic shock refractory to inotropic support and intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) support. Peripheral ECMO can lead to ventricular distention, and IABP..
Lee masAbstract The use of temporary mechanical circulatory support in cardiogenic shock has increased dramatically despite a lack of randomized controlled trials or evidence guiding clinical decision-making. Recommendations from professional societies..
Lee masAbstract Purpose of review Cardiogenic shock is a condition that is characterized by end-organ hypoperfusion secondary to reduced cardiac output, and is associated with substantial mortality. The mainstay of therapy..
Lee masAbstract The Coronary Artery Surgery Study (CASS) trial, which compared the medical and surgical treatment of patients with chronic, stable coronary artery disease, revealed that coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)..
Lee masAbstract The use of venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) following acute myocardial infarction with cardiogenic shock (AMI-CS) is increasing, but the ability to predict favorable outcomes with support remains limited...
Lee masAbstract Although mechanical circulatory support (MCS) has been used to support patients with cardiogenic shock (CS) for many years, recent advances in device technology, together with the lackluster performance of..
Lee masAbstract In patients with severe cardiogenic shock, temporary mechanical circulatory support has become a viable strategy to bridge patients to heart transplantation. However, end-stage heart failure is often associated with progressive organ..
Lee masAbstract Objective Myocardial damage occurs in up to 25% of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases. While veno-venous extracorporeal life support (V-V ECLS) is used as respiratory support, mechanical circulatory support..
Lee masAbstract Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (eCPR) can improve survival in selected patients with cardiac arrest (CA). In this meta-analysis, we evaluated factors associated with short-term survival and favorable neurologic outcome (FNO)..
Lee masAbstract Purpose A survival gap between weaning from venoarterial-extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) and the hospital discharge has been consistently reported. The aim of this study is to investigate the clinical..
Lee masAbstract Temporary mechanical circulatory support can be delivered through a variety of techniques, including percutaneous left ventricular assist devices, surgically implanted rotary pumps, and veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. However, limitations..
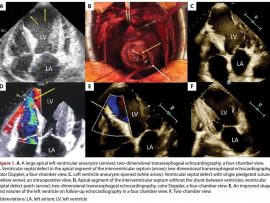
Lee masAbstract Postinfarct ventricular septal defect (PIVSD) is associated with high mortality and the management of these patients has been a challenge with little improvement in outcomes. We commenced a protocol..
Lee masAbstract The Impella mechanical circulatory support (MCS) system is a catheter-based continuous flow cardiac assist device that is widely used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock in medical and surgical cardiac intensive..
Lee masAbstract Introduction Mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices are increasingly used as a treatment option in resuscitation or in patients with cardiogenic shock (CS). Prophylactic implantation in high-risk percutaneous coronary interventions..
Lee masSurvival and Factors Associated with Survival with Extracorporeal Life Support During Cardiac Arrest
Abstract The survival rate after cardiac arrest (CA) remains low. The utilization of extracorporeal life support is proposed to improve management. However, this resource-intensive tool is associated with complications and..
Lee masAbstract OBJECTIVES Implanting a durable left ventricular assist device (LVAD) in a patient on extracorporeal life support (ECLS) is challenging. The goal of this study was to compare..
Lee masAbstract Background Age over 70 years seems to confer poor prognosis for patients under mechanical circulatory support (MCS). Advanced age is usually a relative contraindication. Our objective was to assess the..
Lee masAbstract Background Single-center studies suggest that implementation of multidisciplinary (CS) teams is associated with improved CS survival. Objectives The aim was to characterize practice patterns and outcomes in the management of..
Lee masAbstract Objective: Children requiring multiple consecutive extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) runs likely have ongoing cardiac pathology (eg, residual lesions, myocardial dysfunction) and are exposed to increased complications and end-organ failure...
Lee masAbstract Objective: Children requiring multiple consecutive extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) runs likely have ongoing cardiac pathology (eg, residual lesions, myocardial dysfunction) and are exposed to increased complications and end-organ failure...
Lee masAbstract Background: Adverse neurological events during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) are common and may be associated with devastating consequences. Close monitoring, early identification and prompt intervention can mitigate early and..
Lee masAbstract Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is used in cardiogenic shock refractory to inotropic support and intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) support. Peripheral ECMO can lead to ventricular distention, and IABP..
Lee masReferring to the discussion on effective methods of treatment for patients with a post-infarction left ventricular aneurysm and a ventricular septal defect (VSD) [1], we present the case of a..
Lee masAbstract Improvements in the care of children with cardiomyopathy, CHDs, and acquired heart disease have led to an increased number of children surviving with advanced heart failure. In addition, the..
Lee masAbstract Left ventricular (LV) distention and pulmonary congestion are major complications inherent to venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). This study aimed to quantitatively compare the hemodynamic differences between common circulatory..
Lee masAbstract Thrombosis is a potentially life-threatening complication in veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) circuits, which may originate from the drainage cannula due to unfavorable blood flow dynamics. This study aims to..
Lee masAbstract The rationale for mechanical circulatory support (MCS) in cardiogenic shock is to restore cardiac output in selected patients when critically low or in case of refractory cardiac arrest. Furthermore,..
Lee mas