Abstract Importance Levosimendan may facilitate weaning from venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) and improve survival, but supporting evidence remains limited. Objective To assess whether early administration of levosimendan reduces the time to..
Read MoreAbstract Background For decades, the intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) has been a reliable and readily available pillar of therapy for cardiogenic shock (CS). However, no clinical markers have been validated..
Read MoreAbstract Background Immediate initiation of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has not demonstrated benefit in individuals diagnosed with cardiogenic shock based on the presence of hypotension. The relationship between other hemodynamic..
Read MoreAbstract Background: The use of temporary mechanical circulatory support (tMCS) has revolutionized the management of cardiogenic shock (CS). However, standardized readiness-to-explant criteria for venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) have not been..
Read MoreAbstract Background/Objectives: Mechanical circulatory support (MCS) is increasingly utilized for the management of acute decompensated heart failure (HF) and cardiogenic shock (CS). The primary goals of MCS are to restore systemic..
Read MoreAbstract Background Active mechanical circulatory support (MCS) is associated with high complication rates. Reducing device-related complications may improve outcomes in patients with infarct-related cardiogenic shock (AMI-CS). This study aims to..
Read MoreAbstract Background The experience of a percutaneous microaxial (Impella) in children with is limited. The primary objective of this study was to review our institutional clinical outcomes of Impella use in children..
Read MoreAbstract Background The identification, triage, and management of cardiogenic shock (CS) are complex and resource intensive, particularly given the recent surge in the use of temporary mechanical circulatory support (tMCS)..
Read MoreAbstract Abstract Objectives: To investigate whether severe hyperoxia predisposes to end-organ complications and whether these complications contribute to in-hospital mortality among cardiogenic shock (CS) patients supported in veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane..
Read MoreAbstract Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a state of critical end-organ hypoperfusion caused by primary cardiac failure, in which the heart cannot generate sufficient output despite adequate preload and is associated..
Read MoreAbstract Background Mixed cardiogenic and septic shock has been shown to have a higher mortality than cardiogenic shock alone and presents a unique hemodynamic phenotype. Objectives This study aimed to..
Read MoreAbstract Objectives To describe outcomes in patients who received venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) for cardiogenic shock and to evaluate outcomes following programmatic changes. Design A retrospective cohort study. Setting..
Read MoreAbstract Background: Severe poisoning can lead to catastrophic cardiovascular collapse, often progressing to multiorgan failure and death. While intensive supportive care and pharmacological intervention remain the cornerstone of management, cases of..
Read MoreAbstract Background A systemic inflammatory response can contribute to poor outcomes in an advanced stage of cardiogenic shock (CS). We investigated the efficacy of extracorporeal endotoxin and cytokine adsorption using..
Read MoreAbstract Background Immediate initiation of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has not demonstrated benefit in individuals diagnosed with cardiogenic shock based on the presence of hypotension. The relationship between other hemodynamic..
Read MoreAbstract Background The microaxial flow pump (mAFP) improves survival in selected patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction–induced cardiogenic shock (STEMI-CS). Understanding the impact on cardiac output (CO), cardiac power output..
Read MoreAbstract We investigated echocardiographic and hemodynamic effects of intraaortic balloon pump (IABP) in 26 patients with cardiogenic shock on veno-arterial membrane oxygenation (VA ECMO). Our study demonstrated an 8.1% increase..
Read MoreAbstract While iterative developments have improved outcomes of patients with myocardial infarction, mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction cardiogenic shock (AMI-CS) remains stubbornly high. Several promising treatments have ultimately..
Read MoreAbstract Cardiogenic shock (CS) in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a life-threatening syndrome characterized by systemic hypoperfusion that can quickly progress to multiorgan failure and death. Various devices and configurations..
Read MoreAbstract Background Clinical evidence regarding predictors of successful weaning from mechanical circulatory support (MCS) is lacking. This study aimed to create a simple risk score to predict successful weaning from..
Read MoreAbstract The use of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) for temporary mechanical circulatory support (MCS) is a common treatment in patients with cardiogenic shock (CS) but is associated with high..
Read MoreAbstract Background Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Life Support (VA ECMO) is a critical intervention for patients with cardiogenic shock, serving as bridge to recovery, transplantation, or long-term therapies. The complexity of VA..
Read MoreAbstract Background The impact of intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) on survival and successful bridging to heart replacement therapies (HRT) in patients with heart failure–cardiogenic shock (HF-CS) remains unclear. Objectives The..
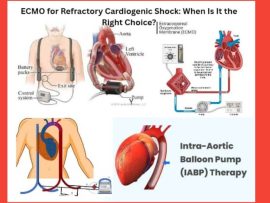
Read MoreIntroduction Refractory cardiogenic shock (RCS) is a life-threatening condition where the heart fails to supply adequate blood flow to the body's organs, despite maximal medical therapy. It is a major..
Read MoreAbstract Background The impact of intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) on survival and successful bridging to heart replacement therapies (HRT) in patients with heart failure–cardiogenic shock (HF-CS) remains unclear. Objectives The..
Read MoreAbstract Background: Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) is increasingly used to treat cardiogenic shock. However, VA-ECMO might hamper myocardial recovery. The Impella unloads the left ventricle. This study aimed to..
Read MoreAbstract Background Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) as rescue therapy for cardiogenic shock (CS) is highly dependent on timeliness and medical resources. Objectives Aimed to assess ECMO management and outcomes in..
Read MoreAbstract Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a critical condition with high mortality, characterized by reduced cardiac output (CO) and tissue hypoperfusion, despite advancements in treatment. Traditional hemodynamic markers like CO measurements,..
Read MoreAbstract Aims Knowing the upper time limit for successful weaning from temporary mechanical circulatory support in cardiogenic shock will help with decision‐making regarding advanced heart failure (HF) therapy or considering..
Read MoreAbstract Cardiogenic shock (CS) is associated with significant mortality. Advances in pharmacological therapies and mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices have markedly improved the therapeutic approach to CS, though treatment efficacy..
Read More