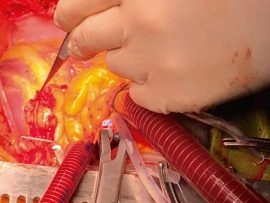
Abstract Objective To compare the application and outcomes of femoral versus axillary arterial cannulation in adult patients undergoing surgery for type A aortic dissection. Methods We conducted a retrospective review..
Read MoreAbstract Objective: Axillary artery cannulation techniques continue to improve and find application throughout cardiac surgery. Yet, early outcomes are poorly documented versus femoral or central arterial cannulation in right minithoracotomy..
Read MoreAbstract Objective: Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) via the right axillary artery (RAA) has become an alternative perfusion strategy, especially in complex aortic procedures. This study delineates our technique and outcome with..
Read MoreAbstract Background Aortic arch disease is a major cause of acute dissections. Surgical replacement is the current curative treatment for aortic arch disease. While traditional aortic cannulation ensures lower body..
Read MoreAbstract Background The site of arterial cannulation is an important consideration in the prevention of cerebral infarction after total arch replacement. We compared the outcomes of cannulation of the bilateral..
Read MoreA variety of cannulation strategies have been used for cardiac surgery interventions throughout the years. In the last 2 decades, a number of studies reported the excellent outcomes of the..
Read MoreAbstract Background This study seeks to assess the outcomes of direct (AX) for . Methods From October 2009 to November 2021 direct AX was planned in 515 patients for thoracic aortic pathology. An important..
Read MoreAbstract Objective Right axillary artery is currently recommended for arterial cannulation in surgery for acute type A aortic dissection. However, the feasibility of cannulation on a dissected right axillary artery..
Read MoreAbstract Objectives In patients with atherosclerotic disease, minimally invasive cardiac surgery using retrograde perfusion for cardiopulmonary bypass via femoral cannulation (FC) carries a higher risk of brain embolization compared with..
Read More