Minimally invasive mitral valve repair (MICS) with neochords combines a precise surgical technique with an advanced perfusion strategy to optimize outcomes. The minimally invasive approach can be performed routinely, delivering..
WeiterlesenIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a cornerstone of modern cardiac surgery, facilitating a bloodless and motionless field for surgeons. Traditionally, hyperoxia—elevated levels of arterial oxygen tension (PaO₂)—has been employed during..
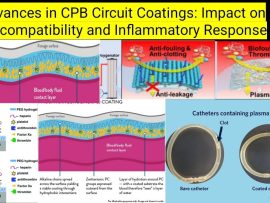
WeiterlesenIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a lifesaving technology in cardiac surgery, but it introduces blood-material interactions that trigger inflammatory and coagulative responses. To address these issues, advancements in biocompatible CPB..
WeiterlesenIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) has transformed cardiac surgery, allowing for safe and controlled procedures on the arrested heart. However, a long-standing debate in perfusion science is whether CPB should be..
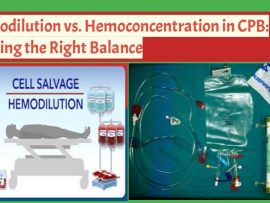
WeiterlesenIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) introduces significant alterations in blood composition due to the priming solution, fluid shifts, and extracorporeal circulation. Hemodilution and hemoconcentration represent two opposing strategies, each with distinct..
WeiterlesenIntroduction Extracorporeal circulation (ECC), used in cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), serves as a temporary replacement for the heart and lungs. It maintains tissue perfusion and gas..
WeiterlesenIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) has been the cornerstone of modern cardiac surgery, allowing for safe cardiac arrest while maintaining systemic perfusion. However, the debate between pulsatile and non-pulsatile flow during..
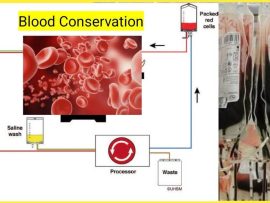
WeiterlesenIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a vital component of cardiac surgery, allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures on a still, bloodless heart. However, CPB is associated with significant hemodilution, coagulopathy,..
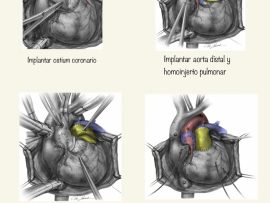
WeiterlesenLeft ventricular outflow tract obstruction in neonates and infants encompasses a variety of anatomical defects, ranging from isolated aortic valve stenosis or discrete subaortic stenosis to the more complex tunnel..
WeiterlesenIntroduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is essential in cardiac surgery, but high-risk patients—such as pediatric, geriatric, and renal-compromised individuals—require specialized priming strategies to optimize outcomes. A one-size-fits-all approach can lead to..
Weiterlesen