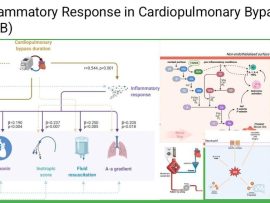
Introduction Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a life-saving technology used in cardiac surgery; however, it triggers a systemic inflammatory response (SIRS) due to blood contact with non-endothelial surfaces, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and..
Lire la suiteAbstract Chen et al. used a rat model of cardiopulmonary bypass followed by 30-min ischemia (induced by ascending aorta blockage) and 15-min reperfusion []. They reported that pyruvate dehydrogenase E1α..
Lire la suiteAbstract Introduction Critically ill patients supported with venoarterial (VA ECMO) are at risk of developing severe arterial , which has been associated with increased mortality. Lower saturation targets in this population may..
Lire la suiteAbstract Although surgical techniques and perioperative care have made significant advances, perioperative mortality in cardiac surgery remains relatively high. Single- or multiple-organ failure remains the leading cause of postoperative mortality...
Lire la suiteAbstract In the United States, about one million people are seen to visit the operating theater for cardiac surgery annually. However, nearly half of these visits result in complications such..
Lire la suiteAbstract Cardiac reperfusion injury is a well-established outcome following treatment of acute myocardial infarction and other types of ischemic heart conditions. Numerous cardioprotection protocols and therapies have been pursued with..
Lire la suiteCyclosporine A-enhanced cardioplegia preserves mitochondrial basal respiration after ischemic arrest
Abstract Background: Mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opening plays a crucial role in cell death during ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). Cyclosporine A (CsA) inhibits mPTP opening. This study aimed to investigate..
Lire la suiteAbstract The protective effects of preprocedural esmolol on myocardial injury and hemodynamics have not, to date, been investigated in patients who were scheduled for cardiac surgeries under a cardiopulmonary bypass..
Lire la suiteAbstract Objective induces in the small . One reason for this damage is a perfusion shift from the muscular toward the mucosal layer. This study investigated the effect of this perfusion shift..
Lire la suiteAbstract Objectives The aim of this pilot study was to elucidate the effects of exogenous (NO) supply to the circuit for cardioprotection against during (CABG) with (CPB). Methods A total of 60 patients with scheduled for..
Lire la suite