Pulmonary artery stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) that occurs in the pulmonary artery, a large artery that sends oxygen-poor blood into the lungs to be enriched with oxygen. The narrowing..
Lire la suiteCervical aortic arch anomaly is a rare congenital entity. The aortic arch extends into the soft tissues of the neck before turning downward on itself to become the descending aorta...
Lire la suiteA rare type of congenital heart disease is an interrupted aortic arch (IAA), which affects approximately 1.5% of congenital heart disease patients. Interrupted aortic arch is an anomaly that can..
Lire la suiteA rare type of congenital heart disease is an interrupted aortic arch (IAA), which affects approximately 1.5% of congenital heart disease patients. Interrupted aortic arch is an anomaly that can..
Lire la suiteA rare type of congenital heart disease is an interrupted aortic arch (IAA), which affects approximately 1.5% of congenital heart disease patients. Interrupted aortic arch is an anomaly that can..
Lire la suiteA rare type of congenital heart disease is an interrupted aortic arch (IAA), which affects approximately 1.5% of congenital heart disease patients. Interrupted aortic arch is an anomaly that can..
Lire la suiteA rare type of congenital heart disease is an interrupted aortic arch (IAA), which affects approximately 1.5% of congenital heart disease patients. Interrupted aortic arch is an anomaly that can..
Lire la suiteInterrupted (IAA) is an extremely rare CHD defined as the loss of luminal continuity between the . Its clinical presentation, including , , or severe CHF in the first 2 weeks of life, is..
Lire la suiteCommon arterial trunk (CAT), or truncus arteriosus, is a rare form of cyanotic congenital heart disease and is highly associated with DiGeorge syndrome (microdeletion 22q11.2). Prenatal diagnosis is highly feasible,..
Lire la suiteEisenmenger syndrome is the most severe form of pulmonary arterial hypertension and arises on the basis of congenital heart disease with a systemic-to-pulmonary shunt. Due to the chronic slow progressive..
Lire la suiteDevelopment of Eisenmenger syndrome in a known patient of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is easy by carefully looking for differential cyanosis and clubbing in upper and lower limbs. It is..
Lire la suiteEisenmenger syndrome (ES) is a constellation of symptoms that arise from a congenital heart defect and result in large anatomic shunts. Due to anatomic variations present at birth, hemodynamic forces..
Lire la suiteAtrial septal defect (ASD) may be rarely associated with Eisenmenger syndrome (ES), the most advanced form of pulmonary vascular disease to complicate a congenital heart disease. In spite of availability..
Lire la suiteAn aortopulmonary (AP) window is a rare cause of Eisenmenger syndrome and results from an abnormal septation of the truncus arteriosus [1]. Most such defects present with early onset congestive heart failure during infancy and adult..
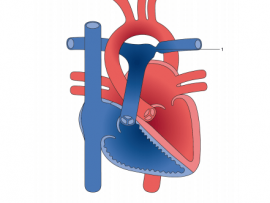
Lire la suiteThe Ebstein's anomaly is a malformation of the tricuspid valve, in which the septal and posterior leaflets are attached to the wall of the right ventricle. The usual association is with an atrial septal defect, followed..
Lire la suiteA malformed heart valve that does not properly close to keep the blood flow moving in the right direction. Blood may leak back from the lower to upper chambers on..
Lire la suiteEbstein’s anomaly is a rare congenital heart disorder occurring in ≈1 per 200 000 live births and accounting for <1% of all cases of congenital heart disease. This anomaly was described..
Lire la suiteMitral valve dysplasia syndrome is a unique form of congenital heart disease with severe aortic stenosis but normal or enlarged left ventricle secondary to primary mitral valve disease. Increased left..
Lire la suiteTransposition of the great arteries (TGA) is a pediatric cardiac congenital defect arising from an embryological discordance between the aorta and pulmonary trunk. During cardiac development, the conotruncal septum spirals..
Lire la suiteTaussig-Bing anomaly is a rare congenital heart malformation that was first described in 1949 by Helen B. Taussig (1898–1986) and Richard J. Bing (1909–). Although substantial improvement has since been..
Lire la suiteDouble outlet right ventricle (DORV) is a heterogeneous group of abnormal ventriculoarterial connections where, by definition, both great arteries (pulmonary artery and aorta) arise primarily from the morphologically right ventricle...
Lire la suiteDouble-outlet right ventricle (DORV) and subaortic ventricular septal defect (VSD) is defined anatomically as a defect where the entire pulmonary trunk and at least half of the aorta arises from..
Lire la suiteThe clinical, hemodynamic, angiocardiographic and pathologic findings are presented in an infrequent but surgically correctable type of double outlet right ventricle. This study is based on six cases, one with..
Lire la suite