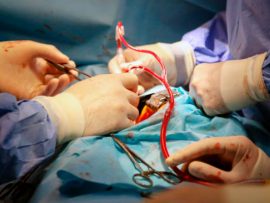
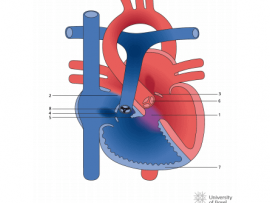
Abstract Background To evaluate the effect and safety of modified ultrafiltration warming technology during pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) surgery. Methods A retrospective analysis included 68 children (<1 year) who..
Lire la suiteAbstract Background The aim of this study is to assess the impact of optimized modified ultrafiltration (OMUF) on the physiological parameters of infants and children undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). Methods..
Lire la suiteAbstract Pediatric Literature As the practice of ultrafiltration arose from pediatric cardiac surgery, much of the evidence to support MUF is from low-powered pediatric studies. Some early, single-center literature, as..
Lire la suiteAbstract Hemodilution and Volume Overload The use of CPB necessitates priming of the CPB circuit, which is typically accomplished using 1-to-2 liters of a crystalloid solution. In addition, 1-to-3 liters..
Lire la suiteAbstract Background: Modified ultrafiltration has been touted as superior to conventional ultrafiltration for attenuating the consequences of hemodilution after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass in children. We conducted a prospective randomized..
Lire la suiteAbstract Conventional ultrafiltration (UF) fails to reverse satisfactorily hemodilution and the rise in total body water (TBW) seen after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). We have modified the technique, timing, and placement..
Lire la suiteAbstract The surgical correction of congenital heart disease using haemodilution and hypothermia with cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) may expose patients to tissue ischaemia and initiate a systemic inflammatory response, increasing the..
Lire la suiteAbstract Total body water (TBW) is increased after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) resulting in tissue oedema and organ dysfunction. Ultrafiltration has been used to reduce this accumulation of water, although conventional..
Lire la suiteAbstract OBJECTIVES Cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery has been associated with several deleterious effects including haemodilution and systemic inflammation. Modified ultrafiltration (MUF) has been well established in paediatric cardiac..
Lire la suiteAbstract Introduction: Modified ultrafiltration (MUF) is employed at the termination of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) in pediatric and neonatal patients undergoing congenital heart surgery to reduce the accumulation of total body..
Lire la suiteAbstract Background Expected benefits of modified ultrafiltration (MUF) include increased hematocrit, reduction of total body water and inflammatory mediators, improved left ventricular systolic function, and improved systolic blood pressure and..
Lire la suiteAbstract OBJECTIVES Cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery has been associated with several deleterious effects including haemodilution and systemic inflammation. Modified ultrafiltration (MUF) has been well established in paediatric..
Lire la suiteAbstract OBJECTIVES Cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery has been associated with several deleterious effects including haemodilution and systemic inflammation. Modified ultrafiltration (MUF) has been well established in..
Lire la suiteAbstract Background: Modified ultrafiltration (MUF) can be performed in infants with ventricular septal defects (VSDs) after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) to reduce haemodilution and its potential adverse effects. High-flow MUF might..
Lire la suiteAbstract Background: This meta-analysis was performed to review the effects of the addition of modified ultrafiltration (MUF) and conventional ultrafiltration (CUF) to CUF alone on postoperative hemoglobin, surgical and ultrafiltration..
Lire la suiteAbstract OBJECTIVES Cardiopulmonary bypass in cardiac surgery has been associated with several deleterious effects including haemodilution and systemic inflammation. Modified ultrafiltration (MUF) has been well established in paediatric cardiac surgery..
Lire la suiteAbstract Objective The aim of this study was to investigate whether the use of at the end of for cardiac surgical procedures significantly changes serum concentrations. Design Prospective study. Setting Single tertiary cardiac..
Lire la suite