Abstract Background Young patients may survive accidental deep hypothermia with prolonged asystolic circulatory arrest because of protective effects of cold. Case Summary An 8-year-old boy fell through pond ice and..
WeiterlesenAbstract Objective The aim of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of lean six sigma management in optimizing the emergency extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) rescue process. Methods The existing..
WeiterlesenAbstract Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) is an established intervention for select patients experiencing refractory cardiac arrest. Among modifiable predictors of survival and neurologic recovery during ECPR implementation, timely restoration of..
WeiterlesenAbstract Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) for refractory cardiac arrest is increasing in usage, but risk factors for seizures are largely unknown. We included adult ECPR patients in the Extracorporeal Life..
WeiterlesenAbstract Introduction Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (eCPR) is a rescue therapy for refractory cardiac arrest, with evidence suggesting improved outcomes when performed at experienced centres. Unlike conventional CPR (cCPR), eCPR patients..
WeiterlesenAbstract Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) brings many monitoring pitfalls due to the countercurrent blood flow, which may create left ventricular overload and perfusion imbalances between the two cerebral hemispheres...
WeiterlesenAbstract Background Prior clinical research demonstrated that rapid reduction in arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is associated with acute brain injury (ABI), which may be..
WeiterlesenAbstract Despite advancements in care, out-of-hospital cardiac arrest has a low survival rate. Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) has shown improved outcomes in select cases, notably in the ARREST trial. However,..
WeiterlesenAbstract Background Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) is increasingly used for refractory cardiac arrest across the world, but its cost-effectiveness remains uncertain. We conducted this systematic review to assess the available..
WeiterlesenAbstract Cardiac arrest outcomes remain historically poor with survival to hospital discharge less than 2.2% in the UK (). Refractory cardiac arrest is characterized by a persistent loss of circulation..
WeiterlesenAbstract Background The optimal low‐flow duration (LFD) for extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) and conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CCPR) remains unclear. We evaluated the impact of LFD on neurological outcomes based on..
WeiterlesenAbstract The use of Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (ECPR) in cases of cardiac arrest is increasing, as addressed in the number of cases in the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) dashboard. Of..
WeiterlesenAbstract Background While the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) has gained increasing attention, its real-world utilization, patient selection, and system-level implementation remain incompletely..
WeiterlesenAbstract Background Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) can improve outcomes in refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), but access is limited by geographic and system constraints. We aimed to compare the potential..
WeiterlesenAbstract Objective To evaluate the effectiveness of venovenous (VV) extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) using a dual-lumen cannula coupled with continuous mechanical chest compressions (cMCC) for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and compare it..
WeiterlesenAbstract BackgroundCPR-induced consciousness (CPRIC) is defined as consciousness during CPR, ranging from eye opening to combative behaviour and vocalisation, despite the absence of spontaneous circulation. CPRIC has not previously been..
WeiterlesenAbstract Introduction Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is an established therapy that supports a patient in respiratory or cardiopulmonary failure to recovery, transplant, or durable mechanical support. Prompt referral by the..
WeiterlesenAbstract Objectives: This study aimed to measure the incidence of postoperative delirium (POD) after aortic arch surgery with hypothermic circulatory arrest (HCA), compare it to cardiac surgeries not requiring HCA, and..
WeiterlesenAbstract Background Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (ECPR) has emerged as a promising intervention for refractory cardiac arrest, with potential benefits in survival and neurological outcomes. However, the impact of ECPR’s rapid,..
WeiterlesenAbstract Objectives Age is the main determinant for mortality in patients requiring postcardiotomy extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (PC-ECMO), but strategies to reverse this trend are unknown. This study investigates PC-ECMO outcomes..
WeiterlesenAbstract After cardiac arrest, restoration of circulation is the first step toward survivorship. Extracorporeal CPR (ECPR), the use of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VA-ECMO) to restore circulation, is increasingly being..
WeiterlesenAbstract Aims Pediatric cardiac arrest is associated with high mortality and significant morbidity among survivors. International guidelines for prognostication remain limited due to small heterogeneous patient populations, variable post-return of..
WeiterlesenAbstract Background Studies have not explored consciousness during deep hypothermic circulatory arrest (DHCA). However, as studies in cardiac arrest have identified a spectrum of consciousness, we sought to establish the..
WeiterlesenAbstract Objectives: Accidental hypothermia has high mortality. Rewarming is the initial primary management strategy. However, detailed evidence on rewarming management is limited, that is, rewarming rate is unclear, particularly with..
WeiterlesenAbstract Introduction Cardiac arrest in the emergency department (ED) is a rare event. Prior studies have used dedicated cardiac arrest registries, but few have leveraged “big data” from electronic healthcare..
WeiterlesenAbstract Objective Cardiac arrest happens in 0.7%-5.2% patients after cardiovascular surgery, and cases with asystole or severe bradycardia need timely temporary pacing. However, routine temporary pacing wire insertion in cardiopulmonary..
WeiterlesenAbstract While iterative developments have improved outcomes of patients with myocardial infarction, mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction cardiogenic shock (AMI-CS) remains stubbornly high. Several promising treatments have ultimately..
WeiterlesenAbstract Rapid hemodynamic stabilization and restoration of pulmonary perfusion are the cornerstones of treatment for high-risk pulmonary embolism (PE). While all current guidelines recommend systemic thrombolysis (SYS) as the first-line..
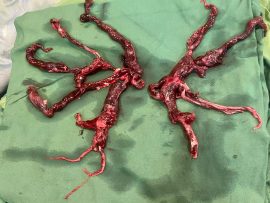
WeiterlesenAbstract Background In refractory cardiac arrest, extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation may increase the survival chance. However, in cases of unsuccessful treatment, extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation may additionally provide an important source of organ donors...
WeiterlesenAbstract Background: Extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (eCPR) is a method for initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass during resuscitation of a patient with refractory cardiac arrest to support end-organ perfusion. This retrospective study evaluates..
Weiterlesen